What is multi-factor authentication, and why is it one of the most important tools in modern cybersecurity? As cyber threats become more sophisticated, relying solely on passwords is no longer enough to protect sensitive information. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring users to verify their identity using two or more methods — such as a password, a smartphone, or a fingerprint. In this guide, we’ll explore what multi-factor authentication is, how it works, and why every individual and organization should be using it to strengthen their digital defenses.What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security process that requires users to verify their identity using two or more independent credentials before accessing a digital system, account, or network. Instead of just asking for a password, MFA combines multiple types of authentication factors to enhance protection against unauthorized access.
In short, when you ask, “What is multi-factor authentication?” — it’s a way to double (or triple) check that you are who you say you are before letting you in.
Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
Understanding what multi-factor authentication is also means understanding why it matters. Passwords alone are no longer enough. They can be guessed, leaked, or stolen. MFA significantly reduces the chances of an account being compromised by adding extra verification layers that are harder for attackers to bypass.
For example, even if someone steals your password, they would still need your fingerprint, security token, or access to your phone to complete the login.
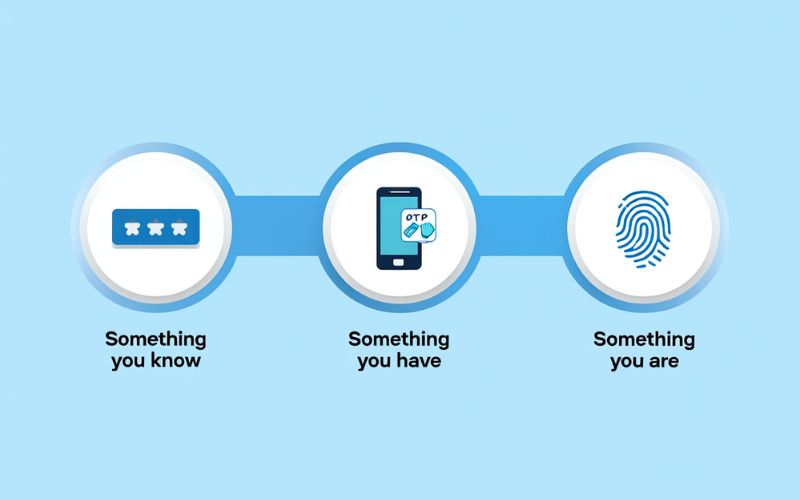
How Does Multi-Factor Authentication Work?
Now that you know what multifactor authentication is, let’s look at how it works.
MFA uses a combination of at least two of the following types of verification:
- Something you know – like a password or a security question.
- Something you have – such as a phone, smart card, or hardware key.
- Something you are – like a fingerprint, facial recognition, or voice.
A common MFA example: You log in with your password (something you know), and then enter a code sent to your phone (something you have).

Real-World Examples of Multi-Factor Authentication
When we ask, what is multi-factor authentication in practice, these are common examples:
- Password + OTP (One-Time Password) sent via SMS or email.
- Fingerprint + phone notification for approval.
- Face ID + PIN code on a mobile banking app.
- Smart card + password in a corporate environment.
These combinations make it much harder for hackers to succeed, even if one factor is compromised.
Types of MFA Authentication Methods

To fully understand what multi-factor authentication is, it’s helpful to break down the common methods used:
- Knowledge-based (what you know): Passwords, PINs, or answers to security questions.
- Possession-based (what you have): Authenticator apps, security tokens, USB keys, or mobile devices.
- Biometric-based (what you are): Fingerprint scans, facial recognition, or voice ID.
Some systems also integrate location-based or behavioral factors, adding even more security by analyzing your device, login time, or IP address.
Adaptive MFA: A Smarter Approach
Adaptive multi-factor authentication (also called risk-based MFA) adjusts its security requirements based on context. For example:
- Logging in from a trusted device at the office? You might only need a password.
- Logging in from a new laptop at midnight from another country? The system may require a second or third factor like a biometric scan or OTP.
This dynamic method improves security without creating unnecessary friction for trusted users.
Is MFA the Same as Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
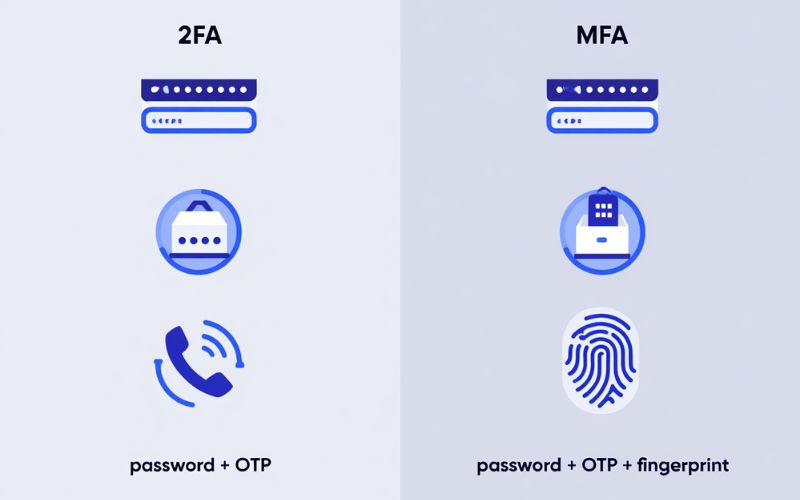
Not quite. When comparing what is multi-factor authentication to two-factor authentication (2FA), the difference is in flexibility:
- 2FA always uses exactly two authentication factors.
- MFA refers to any system that uses two or more factors.
So, 2FA is a type of MFA, but MFA can include three or more layers of protection if needed.
What Is Multi-Factor Authentication in Cloud Security?
In cloud environments, MFA is critical. Users often access systems from outside company networks, making traditional perimeter-based security ineffective. Cloud services like AWS, Google Workspace, and Microsoft 365 all recommend or require MFA to ensure secure remote access.
With MFA, even if someone has a password, they can’t log in without additional verification keeping cloud-based resources safe.
MFA in Microsoft Office 365
Office 365 uses Azure Active Directory for authentication and supports basic MFA options like:
- Microsoft Authenticator app
- SMS verification codes
- Phone calls
- OAUTH tokens
While effective, organizations may need advanced features or broader support. That’s where third-party Identity as a Service (IDaaS) platforms like OneLogin or Okta offer more customizable MFA tools.
More than:
What is Cloud Backup? A Complete Guide for Businesses
What is Subnet Mask? A Beginner-Friendly Guide to IP Networks
Final Thoughts: Why MFA Matters More Than Ever
So, what is multi-factor authentication in today’s digital world? It’s one of the most effective and accessible methods to safeguard systems and sensitive data.
With cyber threats constantly evolving, MFA provides a vital layer of protection against phishing, credential theft, and unauthorized access. By requiring more than just a password, it strengthens your security posture and minimizes the risk of breaches.
Whether you’re securing a personal account or managing enterprise systems, adopting multi-factor authentication is a smart move.
Take control of your digital safety: Don’t wait for a breach to happen. Enable MFA across your key accounts today.
For more insights into cybersecurity tools, digital protection methods, and practical tech advice, explore the Computer tricks section on Softbuzz.net — your trusted source for tech tips and security best practices.



