Did you know that many apps and games fail to connect simply because a hidden firewall rule is silently blocking the port they need? This common issue is one of the top reasons users struggle with slow multiplayer games, broken remote desktop sessions, or software updates that never finish. Understanding how to open a firewall port is the first step to fixing it.
In my years configuring firewalls for both home users and enterprise networks, I’ve seen countless cases where people blame their internet connection—when the real culprit was a closed port. It’s like having a secure front door but never giving your invited guests the key. Without the right port open, even safe and legitimate traffic gets locked out.
This guide is designed to hand you that key. You will learn:
-
What firewall ports are and why they matter in 2025.
-
Step-by-step methods to open ports in Windows, Linux, and routers.
-
How to test, troubleshoot, and secure open ports against misuse.
Let’s unlock the right ports together—so your apps, games, and tools work seamlessly without compromising security.
Key Security Considerations Before You Open a Firewall Port
Opening a firewall port can solve connectivity issues for apps, games, or remote access—but it also exposes your system to higher cybersecurity risks if done carelessly. Each open port creates a potential entry point for hackers, malware, or ransomware. For broader protection strategies, check out our complete guide on firewalls and internet security.
As a cybersecurity professional, I always advise clients to first ask: Do I really need this port open? In many cases, safer alternatives like using a VPN tunnel or Network Address Translation (NAT) rules can achieve the same goal without increasing your attack surface.
Best Practices to Keep Your Firewall Secure
-
Apply the principle of least privilege – only open the exact port needed, and close it when no longer required.
-
Document all firewall changes – keep records for audits, troubleshooting, or rollback.
-
Restrict access to trusted IPs – avoid leaving ports exposed to the entire internet.
-
Back up current firewall rules – export or save your configuration before making edits to prevent accidental lockouts.
By following these safeguards, you’ll maintain strong network security while still enabling the connectivity your apps and services require. According to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, strict change management and least-privilege principles are essential for preventing breaches when modifying firewall rules.

How Firewalls and Port Rules Work: Inbound vs. Outbound Explaine
Firewall rules work in two directions: inbound rules control traffic entering your system, while outbound rules manage data leaving your device. Configuring both correctly is essential for secure and efficient network communication. For readers new to the basics, see our full guide on what is a firewall to understand how firewalls function at a fundamental level.
A firewall doesn’t just decide whether to allow or block traffic—it also distinguishes between inbound (incoming) and outbound (outgoing) connections. As someone who has configured firewalls for both enterprise servers and home networks, I’ve seen many security issues arise simply because admins misunderstood this difference.
-
Inbound rules protect your system from external threats. For example, opening port 3389 (RDP) allows remote desktop access, but if left unmanaged, it could expose you to cyberattacks.
-
Outbound rules regulate data your apps send out. A common case is permitting a software updater to connect via port 443 (HTTPS). Restricting outbound rules is a smart way to prevent malware from “phoning home.”
By clearly understanding inbound vs. outbound port rules, you ensure your firewall is configured to support legitimate apps while keeping attackers out. This distinction is one of the core skills every IT admin, gamer, or home user needs when learning how to open a firewall port safely in 2025.
How to Open a Firewall Port in Windows (2025)
To open a firewall port in Windows 10/11, use Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security to create an inbound or outbound rule, select the protocol (TCP/UDP), enter the port number, and allow the connection.
Opening a firewall port in Windows is a common task for gamers, IT professionals, and remote workers who need applications like RDP, Minecraft servers, or VPN tools to function correctly. From my experience managing enterprise and home setups, the most frequent mistakes are choosing the wrong protocol or forgetting to apply the rule to all network profiles. Below is the complete step-by-step method.
Step-by-Step: Open a Firewall Port in Windows 10/11
-
Open Windows Defender Firewall – Search “Windows Defender Firewall” in the Start menu.
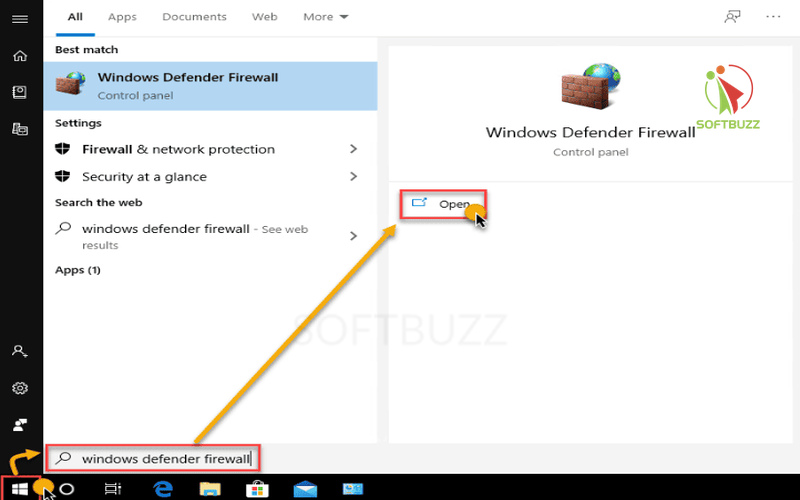
Open Windows Defender Firewall -
Access Advanced Settings – Select Advanced Settings to launch Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security.
-
Create a New Rule – Choose Inbound Rules or Outbound Rules (depending on the need), then click New Rule….
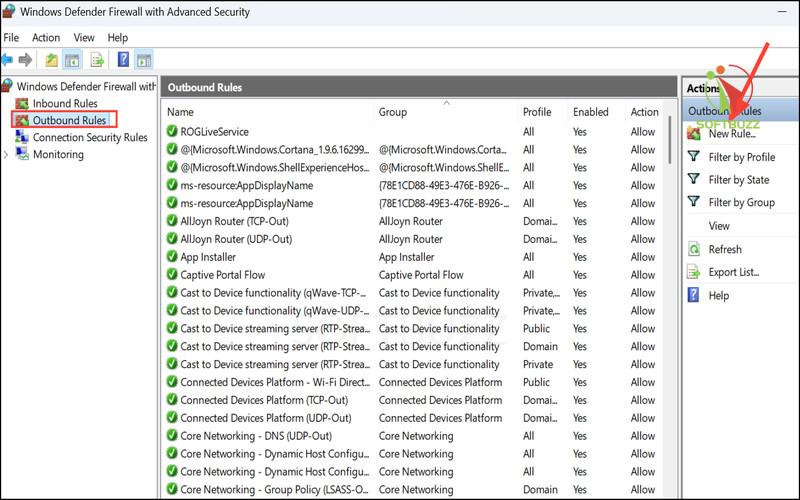
Click New Rule -
Choose Rule Type – Select Port → click Next.
-
Select Protocol and Port – Pick TCP or UDP, then enter the port number (e.g., 3389 for RDP, 25565 for Minecraft).
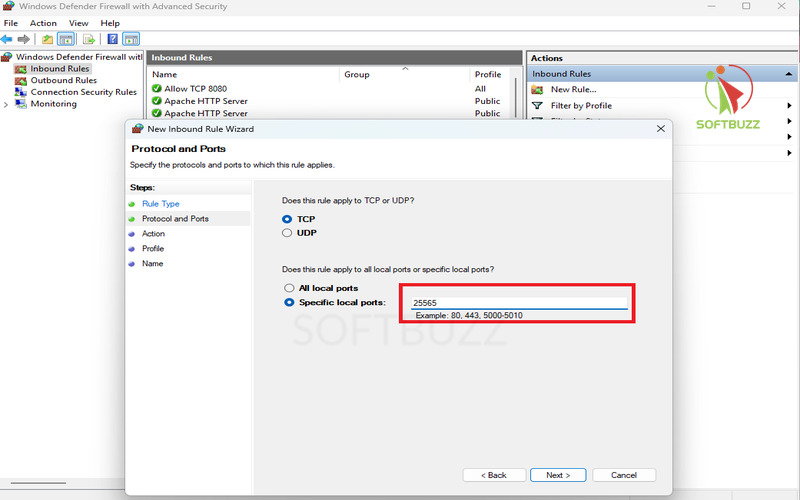
Select Protocol and Port -
Allow the Connection – Select Allow the connection.
-
Select Profiles – Apply to Domain, Private, Public for full coverage.
-
Name the Rule – Example: “Block or Allow RDP 3389.”
Tip for IT admins: You can later edit, disable, or delete rules in the list.
PowerShell Shortcut for Advanced Users
Instead of the GUI, open PowerShell and run: New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Allow TCP 8080" -Direction Inbound -LocalPort 8080 -Protocol TCP -Action Allow
This method is scriptable, repeatable, and ideal for enterprise deployments where consistent firewall configurations are required.
Troubleshooting Common Errors When Opening Firewall Ports (Windows)
-
Rule not working – Confirm the right port and protocol (TCP/UDP).
-
App not running – The service must actively listen on the port.
-
Conflicting security software – Antivirus or third-party firewalls may override rules.
-
Wrong profile – Ensure the rule matches your active network (Private, Public, Domain).
Verification: Use Test-NetConnection in PowerShell or an online port scanner to confirm results whenever you apply guides on how to open a firewall port.
How to Open a Firewall Port in Linux (UFW, firewalld, iptables)
To open a firewall port in Linux, use UFW on Ubuntu/Debian (sudo ufw allow PORT/tcp), firewalld on CentOS/Fedora (sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=PORT/tcp), or iptables for advanced setups (sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport PORT -j ACCEPT). Always verify with status commands.
Knowing how to open a firewall port in Linux is essential for admins running game servers, web apps, or remote access services.
For Linux users, how to open a firewall port in Ubuntu, Debian, or CentOS is an essential skill for running game servers, web applications, or remote access tools. Whether you use UFW, firewalld, or iptables, learning how to open a firewall port in Linux gives you full control over connectivity and security.
Open a Firewall Port with UFW (Ubuntu/Debian)
For beginner-friendly systems like Ubuntu or Debian, UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) is the default.
This allows TCP traffic on port 8080 and confirms it’s active.
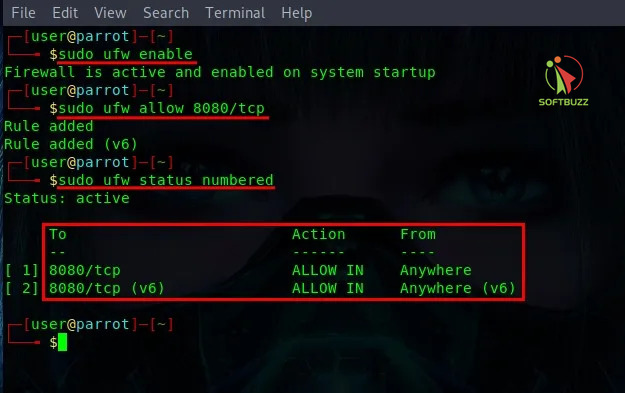
Open a Firewall Port with firewalld (CentOS/RHEL/Fedora)
firewalld offers zone-based management, ideal for enterprise servers.
Many admins practicing how to open a firewall port on Red Hat systems prefer firewalld for its flexibility.
The --permanent flag ensures the rule persists after reboot.
Open a Firewall Port with iptables (Advanced/Legacy Distros)
For legacy or advanced setups, iptables provides full control.
Mastering iptables is a must if you want to fully understand how to open a firewall port at the most granular level.
To remove the rule:
Always save rules (sudo iptables-save) so they persist after restart.
Best Practices for Linux Firewall Ports
-
Open only the necessary ports (least privilege principle). External scans are also a great way to double-check your process after you learn how to open a firewall port.
-
Document all rules for troubleshooting and compliance.
-
Restrict access by IP address where possible.
-
Regularly audit firewall configurations following CIS Benchmarks and NIST guidelines.
How to Check If a Firewall Port is Open (Verification Methods)
To check if a firewall port is open, use netstat or Test-NetConnection in Windows, ss or lsof in Linux, or an online port scanner like canyouseeme.org. Always confirm the app is running and firewall rules are correct.
Verifying that your firewall port is open is a critical step after making configuration changes. From my experience managing both home networks and enterprise firewalls, many troubleshooting issues come from simply not confirming whether the service is actually listening on the expected port. Here’s how you can verify across platforms.
Check Firewall Ports on Windows
Use built-in tools to confirm open ports:
-
Command Prompt:
netstat -an | find "PORT" -
PowerShell (Windows 10/11):
Test-NetConnection -Port PORT_NUMBER -ComputerName localhost
This ensures the rule is active and the application is listening.
Check Firewall Ports on Linux
Linux provides multiple utilities to test ports:
-
ss command:
ss -tuln | grep PORT -
lsof command:
lsof -i :PORT
Both confirm whether a process is bound to the port.
Use Online Port Scanners (External Testing)
Tools like canyouseeme.org or Nmap can test from outside your network. This helps confirm if the port is publicly accessible.
Caution: Be mindful of privacy and only use trusted services when testing from external sources.
Why a Firewall Port Might Appear Closed
If your port isn’t showing as open, common reasons include:
-
The application/service isn’t running or bound to the port.
-
A local or upstream firewall is blocking the connection.
-
Incorrect rule configuration (wrong protocol, scope, or profile).
Pro Tip: Always document open ports, run periodic scans, and review every step of how to open a firewall port to avoid mistakes.
When and How to Use Router Port Forwarding (vs. Firewalls)
Firewall rules control traffic on your device or network perimeter, but they do not automatically forward external requests through your router to a specific internal IP. Port forwarding on routers redirects traffic coming from outside your local network to a designated internal device and port.
Port forwarding is essential when you want to expose services like game servers, home automation, or remote desktop over the internet.
Basic setup steps:
- Access your router’s admin interface via its IP address (commonly 192.168.1.1).
- Locate the “Port Forwarding” or “Virtual Server” section.
- Enter the external port, internal IP address of your device, and the internal port number.
- Save and apply the settings.
Be cautious exposing ports to the internet; only forward ports necessary for your use case and ensure devices are secured to prevent unauthorized access. Many router interfaces even include simple wizards that teach beginners how to open a firewall port safely.
Frequently Asked Questions & Troubleshooting About Opening Firewall Ports
Opening a firewall port can improve app connectivity, but it must be done securely. Follow best practices: only open necessary ports, restrict access to trusted IPs, and close unused ones promptly.
Q1: When following guides on how to open a firewall port, is it safe?
A: Yes—when configured properly. Opening only the ports required for specific apps (e.g., gaming or VPNs) is safe. Always limit exposure by:
-
Applying the principle of least privilege.
-
Restricting access to specific IP ranges.
-
Monitoring logs for suspicious activity.
According to NIST Cybersecurity Framework, misconfigured open ports are one of the top causes of breaches.
Q2: What is a port number?
A: A port number is a unique identifier that directs network traffic to the correct service or process. Examples:
-
80 (HTTP) for websites.
-
443 (HTTPS) for secure browsing.
-
3389 (RDP) for remote desktop.
Q3: What’s the difference between TCP and UDP?
A:
-
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): Reliable, connection-oriented, ensures ordered packet delivery (e.g., web browsing, email).
-
UDP (User Datagram Protocol): Faster, connectionless, less reliable but efficient (e.g., gaming, video streaming).
Q4: Which ports should never be opened to the public?
A: Avoid exposing sensitive management or database ports directly to the internet, such as:
-
22 (SSH)
-
3306 (MySQL)
-
1433 (SQL Server)
If required, secure them with VPN tunneling, MFA, or IP whitelisting.
Q5: What’s the difference between opening a port and port forwarding?
A:
-
Opening a port: Allows traffic through your device’s firewall.
-
Port forwarding: Configures your router to redirect external traffic to a specific internal IP/port (used for game servers, remote access, IoT).
Q6: How do I close or undo a firewall port opening?
A:
-
Windows: Open Windows Defender Firewall → Advanced Settings → Rules, then disable or delete the rule.
-
Linux: Use
ufw delete allow <port>or remove the iptables/firewalld rule. -
Router: Remove or disable the port forwarding entry in the admin interface.
Pro Tip: Always document firewall changes and perform regular audits. Closing unused ports immediately is recommended by CIS Controls v8 to reduce attack surface.
Conclusion
Opening a firewall port in Windows, Linux, or routers can unlock apps, games, and remote tools—but it must be done securely to avoid risks.
Opening firewall ports is an essential skill in 2025 for anyone running applications, multiplayer games, or remote access services. Done correctly, it enables smooth connectivity; done carelessly, it can expose your system to cyber threats. The key is balancing functionality with security:
-
Understand inbound vs. outbound firewall rules before making changes.
-
Follow step-by-step guides for your platform (Windows, Linux, or router).
-
Verify open ports with testing tools to ensure rules are working as intended.
-
Always document changes, apply the principle of least privilege, and close ports no longer in use.
-
Where possible, consider safer alternatives like VPNs or NAT instead of leaving ports open.
With careful management, router port forwarding, and adherence to NIST and CIS best practices, you can maintain a secure, reliable, and optimized network environment for both personal and business use.
For more step-by-step tutorials, explore our Windows category or return to the Softbuzz homepage for the latest cybersecurity tips and practical guides.










