What is Device Manager used for? It is a vital Windows utility that enables users to view, control, and troubleshoot all hardware components connected to their computer. Since its introduction in Windows 95, Device Manager has served as a centralized tool for managing drivers, identifying hardware conflicts, and ensuring devices operate correctly. Whether you’re looking to update a driver, disable a malfunctioning component, or verify if Windows detects a specific device, Device Manager provides an intuitive interface to handle these tasks. This guide will walk you through its core functions, key features, and practical ways to use it for system maintenance and hardware issue resolution.
What is Device Manager Used For? (Core Functions & Purposes)
Device Manager primarily serves as the hub for managing all hardware components on a Windows system, delivering several key functions:
- Viewing Hardware: Displays a detailed device tree categorizing all internal and external hardware, including CPUs, GPUs, USB devices, and peripherals.
- Managing Drivers: Lets users install, update, roll back, or uninstall device drivers, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility.
- Enabling/Disabling Devices: Allows temporary deactivation of hardware components to troubleshoot conflicts or conserve resources.
- Troubleshooting Hardware Issues: Flags devices with warning icons indicating malfunctions or driver problems.
- Viewing Device Status: Provides detailed information about each device’s operational state and driver details.
- Resolving Conflicts: Helps identify and address resource conflicts such as IRQ or memory address overlaps.
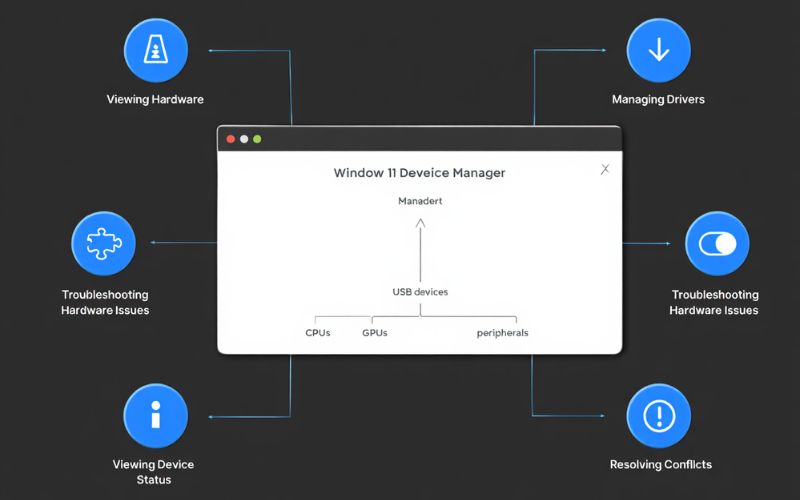
Device Manager showing hardware categories
For instance, if a graphics card driver is outdated or causing display problems, Device Manager facilitates easy updates. Similarly, a malfunctioning USB device can be disabled or reinitialized here to restore proper functionality. These uses highlight why Device Manager is integral to both everyday users aiming to keep their systems running smoothly and IT professionals tasked with maintaining complex environments.
30+ Things You Can Do With Device Manager
- View all installed hardware – Access a structured list of every device connected.
- Update drivers – Search for and install the latest drivers for better stability.
- Roll back drivers – Restore previous driver versions when updates cause issues.
- Uninstall devices – Remove device records to fix persistent errors.
- Disable devices – Temporarily turn off hardware to isolate problems.
- Enable devices – Reactivate previously disabled hardware.
- Scan for hardware changes – Detect newly connected devices or removed hardware.
- View device properties – Check driver version, resources, and status details.
- Identify resource conflicts – Analyze IRQ, DMA, or memory clashes affecting device operation.
- Access events log – Review device-related events for troubleshooting.
- View hidden devices – Reveal non-present or phantom devices that still have drivers installed.
- Export device tree – Save the hardware configuration for documentation or auditing.
- Change hardware IDs – Manage device identification for specific configurations.
- Force driver signature enforcement – Manage driver verification policies.
- Set device power management options – Configure sleep or wake behaviors.
- Access driver details – Review files associated with installed drivers.
- Update firmware (where supported) – Trigger firmware updates through device properties.
- View device manufacturer info – Verify OEM details and device origin.
- Manage USB devices – Troubleshoot and reset USB controllers and hubs.
- Control hidden system devices – Manage devices not typically visible in other parts of Windows.
- Access context menu actions – Quickly update, disable, or uninstall devices via right-click.
- Restore default hardware configurations – Reset devices recognized with incorrect settings.
- Check device driver dates – Assess driver currency for updates.
- View driver provider – Identify if a driver is from Microsoft or a third party.
- Assign or change drive letters – For removable drives (indirectly, via device properties).
- Manage audio devices – Enable/disable sound hardware components.
- Troubleshoot network adapters – Restart or reset adapters to fix connectivity issues.
- Identify unknown devices – Use hardware IDs for identification.
- Configure PCI devices – Adjust allocation for certain PCI components.
- Run hardware diagnostics – Launch tests or linked tools through device properties.
- Monitor device performance alerts – Detect issues flagged by Windows kernel or driver subsystems.
How Device Manager Works: Features, Interface, and Navigation
The Device Manager interface presents a hierarchical device tree categorized by hardware types such as “Display adapters,” “Network adapters,” “Disk drives,” and more. Each category expands to show individual devices, with corresponding icons indicating device status. A yellow exclamation mark signals driver or hardware problems, while a red X denotes a disabled device.
Right-clicking on any device reveals a context menu with options like “Update driver,” “Disable device,” “Uninstall device,” and “Properties.” The Properties dialog offers multiple tabs displaying detailed information: General (device status), Driver (driver details and update options), Events (device logs), and Resources (hardware resource allocations).
Advanced users can enable “Show hidden devices” via the View menu to reveal unused, non-present, or ghost devices. Additionally, options exist for accessing device-specific troubleshooting tools. The UI is designed to balance simplicity for casual users with deeper exploration capabilities for IT professionals.

Real-World Use Cases & Scenarios
Device Manager’s versatility makes it invaluable across various real-world contexts:
- Updating Drivers: A home user notices graphics glitches post Windows update. Updating the GPU driver via Device Manager.
- Fixing Unrecognized USB Devices: A peripheral is not detected. Disabling and re-enabling the USB controller via Device Manager resolves the issue without reboot.
- Disabling a Network Adapter: An IT admin temporarily disables a wireless network adapter during troubleshooting of conflicting network interfaces on a corporate laptop.
- Troubleshooting Post-Update Issues: After a Windows patch, a webcam stops working. Device Manager reveals a driver conflict and allows rollback to a stable driver version.
- Identifying Unknown Devices: After installing new hardware, the device shows as “Unknown.” Using Device Manager’s hardware IDs, the user searches online to find and install the correct drivers.
- Checking Device Status: A printer intermittently fails to connect. Device Manager’s status tab reveals a resource conflict, enabling targeted resolution.
- Enabling Hidden Devices: An IT technician uncovers ghost devices that interfere with system stability and cleans them up remotely.
These examples underscore Device Manager’s practical roles in both everyday computing and professional IT environments.

Step-by-Step Guide: Using Device Manager
Opening Device Manager:
- Press Windows + X and select “Device Manager” from the menu.
- Or, type devmgmt.msc in the Run dialog (Windows + R) and press Enter.
- Search for “Device Manager” via the Windows Start menu or Settings’ Device section.
Locating and Identifying Device Issues:
- Expand device categories to locate hardware components.
- Look for warning icons (yellow exclamation or red X) indicating issues.
- Right-click the device and select Properties to view detailed status and error codes.
Updating, Rolling Back, or Uninstalling Drivers:
- Right-click the device and select Update driver to download new drivers automatically or browse manually.
- To undo a problematic update, choose Properties -> Driver tab -> Roll Back Driver.
- Uninstall devices via right-click to remove drivers completely, then scan for hardware changes to reinstall.
Disabling/Enabling Devices:
- Right-click a device and select Disable device to deactivate temporarily.
- Use Enable device to reactivate as needed.
Checking Device Properties and Status:
- Access device Properties to check driver provider, version, hardware IDs, and resource usage.
- Use the Events tab for recent device-related logs for advanced troubleshooting.
Error Code Lookup: Device Manager error codes (e.g., Code 10, 43) provide clues to specific faults. Use Microsoft’s official documentation or error lookup tools to interpret codes accurately for effective fixes.
Advanced Device Manager: For IT Pros and Power Users
Beyond basic management, Device Manager integrates with enterprise-grade tools and scenarios:
- Remote Device Management: IT administrators use MMC (Microsoft Management Console) snap-ins or Group Policy to manage devices Windows-wide remotely.
- Command-Line Access: Tools like DevCon and PowerShell scripts automate device management tasks at scale.
- Group Policy Integration: Enforce driver installation rules and device restrictions across corporate networks.
- Professional Troubleshooting: Combined with SysInternals Suite and network diagnostics, Device Manager helps isolate hardware-related network outages or driver conflicts.
- Limitations: Device Manager does not support deep hardware diagnostics or remote troubleshooting of devices beyond local control and lacks visibility into non-Windows environments.
These capabilities enable administrators to maintain large fleets of systems efficiently while acknowledging Device Manager’s scope as part of a broader IT toolkit.
What Device Manager Can and Cannot Fix
| Issues Device Manager Can Fix | Issues Beyond Device Manager’s Scope |
| Driver installation and updates | Physical hardware malfunctions or damage |
| Enabling/disabling devices causing conflicts | Firmware corruption requiring manufacturer tools |
| Resolving resource conflicts (IRQ, DMA) | Physical hardware component replacement or upgrades |
| Resetting device status and removing phantom devices | Operating system corruption or file system errors |
| Identifying unknown devices via hardware IDs | Network-wide device management beyond local computer |
| Optimization/TRIM for SSDs |
While Device Manager is a powerful utility for software-level fixes and managing device integration with Windows, it cannot repair damaged physical components or fix deep-seated OS-level problems. Users should exercise caution when disabling or uninstalling devices, always creating restore points or backups to avoid unintentional disruption.
Device Manager and System Health: Performance, Compatibility, and Security
Regular use of Device Manager contributes significantly to system health by:
- Maintaining Up-to-Date Drivers: Updated drivers improve compatibility, stability, and performance, reducing system crashes and unexpected behavior.
- Preventing Hardware Conflicts: Identifying and resolving resource allocation issues minimizes device failures.
- Enhancing Security: Disabling unused or vulnerable physical ports (such as FireWire or old network adapters) reduces the system’s attack surface.
- Optimizing Boot Times: Removing unnecessary or malfunctioning device drivers accelerates startup processes.
Microsoft recommends proactive hardware management through Device Manager to ensure peak system health, especially in environments where reliability and security are paramount.
Supplementary Insights: Frequently Asked Questions About Device Manager
Can I use Device Manager without administrator rights?
Typically, administrative privileges are required to modify devices, including updating or disabling drivers. Viewing device information may be possible with limited rights.
Is Device Manager available on all versions of Windows?
Device Manager has been included in all major Windows releases since Windows 95, including Windows 10 and 11.
What’s the difference between Device Manager and Device Setup?
Device Manager focuses on listing and managing installed hardware, whereas Device Setup (Setup API) handles device installation processes programmatically.
Can Device Manager fix driver signature issues?
Device Manager itself cannot bypass driver signing policies but can help identify problematic drivers that trigger signature enforcement errors.
Is it safe to uninstall devices via Device Manager?
Yes, but it should be done cautiously; uninstalling critical drivers can lead to system instability. Always create backups or restore points before major changes.
Further Reading, Tools & Resources
For deeper understanding and technical assistance, consider these authoritative resources:
- Microsoft Device Manager Documentation: Official guide for Device Manager operations and error codes on Microsoft Docs.
- TechNet Forums: Community-driven troubleshooting and best practices for Windows hardware management.
- SysInternals Suite: Advanced diagnostic tools from Microsoft for hardware and system utilities.
- DevCon Utility: Command-line device manager for scripting and automation.
- Driver Booster and Snappy Driver Installer: Free tools for automated driver updates.
These resources complement the foundational knowledge provided here, enabling users to harness Device Manager’s full potential with confidence and security.
Conclusion
What is Device Manager used for? It is a powerful Windows utility that plays a key role in managing, diagnosing, and optimizing hardware functionality at the software level. From resolving driver issues to monitoring device status, Device Manager helps users maintain a stable and responsive computing environment. While it can’t fix physical hardware problems, its ability to detect, control, and troubleshoot connected devices makes it a crucial part of any system maintenance toolkit, especially in the increasingly complex digital landscape of 2025.
To keep your PC running smoothly and avoid costly downtime, make Device Manager part of your regular troubleshooting routine. For more expert tips and detailed Windows guides, don’t forget to explore the Software section on Softbuzz.










