Have you ever noticed your computer gradually becoming slower—taking longer to start up, load applications, or save files? You might be dealing with a common yet overlooked issue called disk fragmentation.
But what is disk fragmentation, exactly, and why should you care?
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about this hidden performance killer: how it happens, why it slows your system down, and what you can do to fix it. We’ll also share real user stories to highlight just how much of a difference defragmentation can make in everyday computing.
Let’s explore how to bring your PC back to life-starting with understanding fragmentation.
1. What Is Disk Fragmentation?
Disk fragmentation occurs when a file is broken into pieces to fit on the disk. As you save, modify, and delete files, your hard drive can become cluttered, causing files to be stored in non-contiguous sectors. This fragmentation means the read/write head of the disk has to move more to access the entire file, leading to slower performance.
Think of it like a puzzle: if all the pieces are scattered, it takes longer to assemble the picture. Similarly, a fragmented disk requires more time to read and write files, slowing down your computer.

2. How Does Disk Fragmentation Affect Performance?
When files are fragmented, your hard drive’s read/write head must move to different locations to access the entire file, increasing the time it takes to open or save files. This can lead to:
-
Longer boot times
-
Slower application launches
-
Delayed file access
-
Overall system sluggishness
3. Real User Experiences: The Impact of Fragmentation
“I noticed my computer was taking forever to start up and open files. After running a defragmentation tool, the improvement was night and day.”
“Regular defragmentation has become part of my maintenance routine. It keeps my system running smoothly.”
These anecdotes highlight the tangible benefits of addressing disk fragmentation.
4. Causes of Disk Fragmentation
Several factors contribute to disk fragmentation:
-
Frequent file modifications
-
Installing and uninstalling programs
-
Insufficient disk space
-
Saving large files with limited contiguous space
5. Identifying Disk Fragmentation
Use your OS’s built-in analysis tools. On Windows:
-
Press Windows + S and type Defragment and Optimize Drives.
-
Select your drive → click Analyze.
-
If fragmentation >10%, proceed with defragmentation.
6. How to Defragment Your Disk
If you’ve discovered that your hard drive is fragmented, don’t worry—defragmentation is not only easy but also highly effective. You can choose between using built-in system tools or third-party software depending on your level of experience and performance needs.
Below are the two main approaches, each with their own pros and ideal use cases:
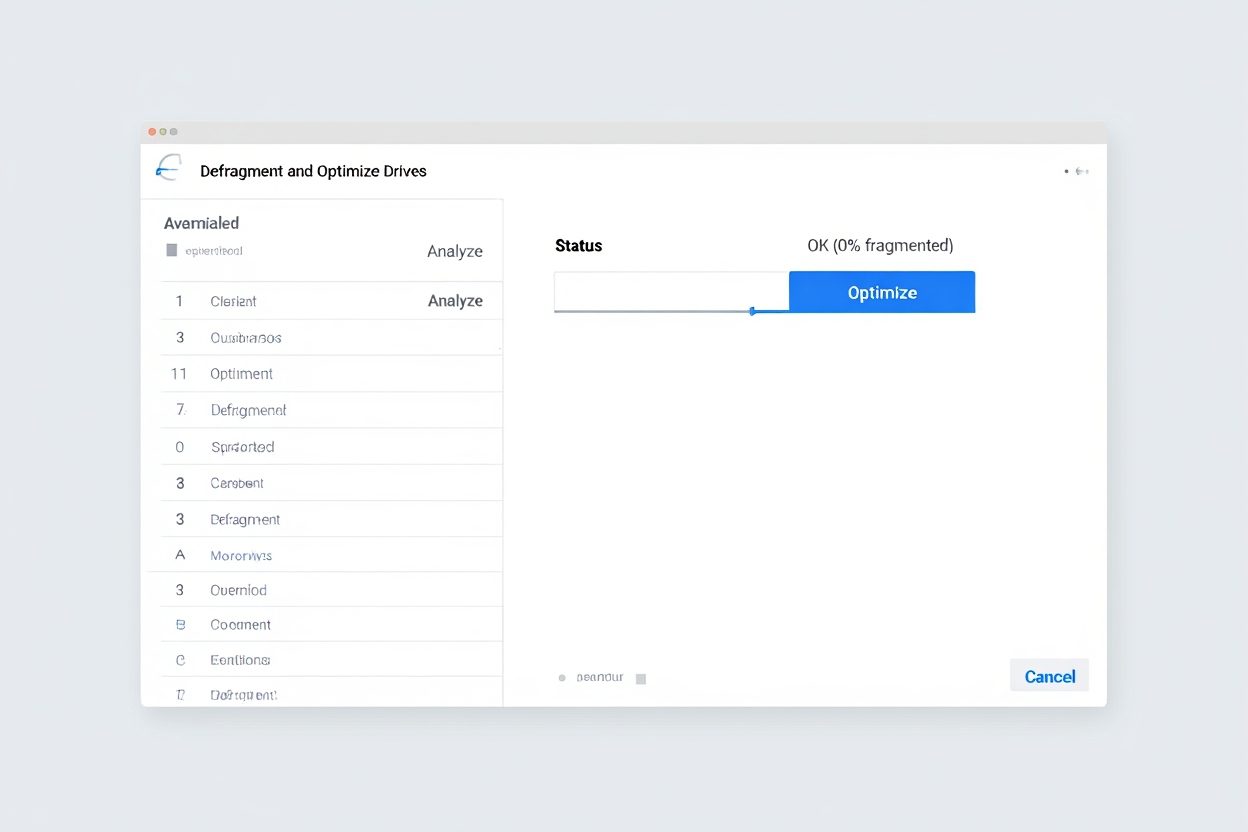
6.1. Using Built-in Tools (Recommended for Most Users)
Most modern operating systems include defragmentation utilities that are easy to use, safe, and integrated with system settings:
Windows (10/11/8)
Windows comes with a tool called “Defragment and Optimize Drives”.
To use it:
-
Press
Windows + S, type “Defragment”, and open Defragment and Optimize Drives. -
Select your target drive (usually C:).
-
Click Analyze to check fragmentation level.
-
If it’s over 10%, click Optimize to begin defragmentation.
Tip: Windows automatically runs weekly optimization by default. You can change this schedule under the “Change settings” option.
MacOS
Modern macOS versions using APFS (Apple File System) don’t require manual defragmentation. The file system is designed to avoid fragmentation, and background processes handle optimization automatically.
Unless you’re using a very old version of macOS or an HDD formatted with HFS+, you don’t need to worry about fragmentation on Macs.
Linux
Linux file systems like ext4 are highly efficient at avoiding fragmentation. Manual defragmentation is rare and typically unnecessary, though advanced users can use tools like e4defrag if needed. Running manual defragmentation is generally discouraged as it rarely provides benefits on modern Linux file systems.
6.2. Using Third-Party Defragmentation Software
If you’re looking for more control or faster optimization, third-party defragmentation tools can offer additional features like boot-time defrag, visual fragmentation maps, or the ability to defrag specific files and folders.
Here are a few trusted options:
Defraggler (by CCleaner)
-
Clean, user-friendly interface
-
Allows defragmentation of individual files/folders
-
Portable version available
Auslogics Disk Defrag
-
Fast defragmentation with intelligent file placement
-
Boot-time defrag option
-
Includes disk health monitoring
Smart Defrag (by IObit)
-
Auto-defrag in the background while system is idle
-
Game optimization mode
-
Scheduled defragmentation
Always download third-party software from the official websites to avoid bundled ads or malware.
Whether you’re a casual PC user or a system admin, choosing the right tool based on your workflow can make defragmentation simple, safe, and incredibly beneficial.
Read more:
- What is a Virtual Desktop? Everything You Need to Know in 2025
- What is a Shortcut Key? Definition, Examples & Guide (2025)
- What is BIOS? Everything You Need to Know
- What Is a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)? Causes, Fixes, and Real Experiences
7. Preventing Disk Fragmentation
Now that you know how to defragment your hard drive, the next logical step is preventing fragmentation from building up in the first place. While it’s nearly impossible to stop it entirely, especially on traditional HDDs. There are several simple habits you can adopt to reduce its frequency and impact.
Here are some practical tips to help you minimize disk fragmentation over time:
-
Maintain at least 15–20% free disk space: This gives the system enough room to store files contiguously.
-
Clean up junk and temporary files regularly: Use built-in tools like Disk Cleanup or third-party cleaners.
-
Avoid frequent installation/uninstallation of large applications: These actions often leave fragmentation gaps.
-
Defragment on a schedule: Most systems allow automated defragmentation weekly or monthly, take advantage of it.
-
Store large files mindfully: When possible, keep media and backups on secondary drives to reduce clutter on your main disk.
These small steps can go a long way in keeping your system healthy, saving you from the frustration of slowdowns and system delays.
8. SSDs and Fragmentation: A Different Story
SSDs don’t suffer from fragmentation the way HDDs do. Their performance is based on access time, not mechanical movement. In fact, when maintaining SSDs, the OS runs a process called ‘re-trim’ or ‘optimization,’ rather than defragmentation, to maintain its health and lifespan. Modern OSs use TRIM to manage this efficiently.
9. Conclusion
Understanding what is disk fragmentation can be a game-changer for anyone using a traditional hard drive. Fragmentation silently slows your system down over time, but with the right knowledge and tools, you can keep your PC running smoothly and efficiently.
At Softbuzz, we believe that tech tips should be practical, clear, and genuinely helpful. That’s why we’re here to guide you through everything from disk cleanup to system performance tuning.
Want to learn more ways to optimize your computer?
Explore our Computer Tricks section for expert guides and actionable solutions that make tech easier.
Got questions about fragmentation or your PC’s speed? Drop a comment below. We’d love to help you troubleshoot and speed things up!










