Ever clicked a button on a website and felt like the response took forever—even though your internet seemed fine? That lag might be caused by something you can’t see, but definitely feel: network latency.
If you’ve ever asked yourself, what is network latency, you’re not alone. It’s one of the most overlooked factors affecting everything from web browsing to video calls, gaming, and cloud-based work. In this guide, we’ll explain what network latency is, what causes it, how it affects your digital life, and how to fix it—based on both real-world experience and industry best practices.
1. What Is Network Latency?
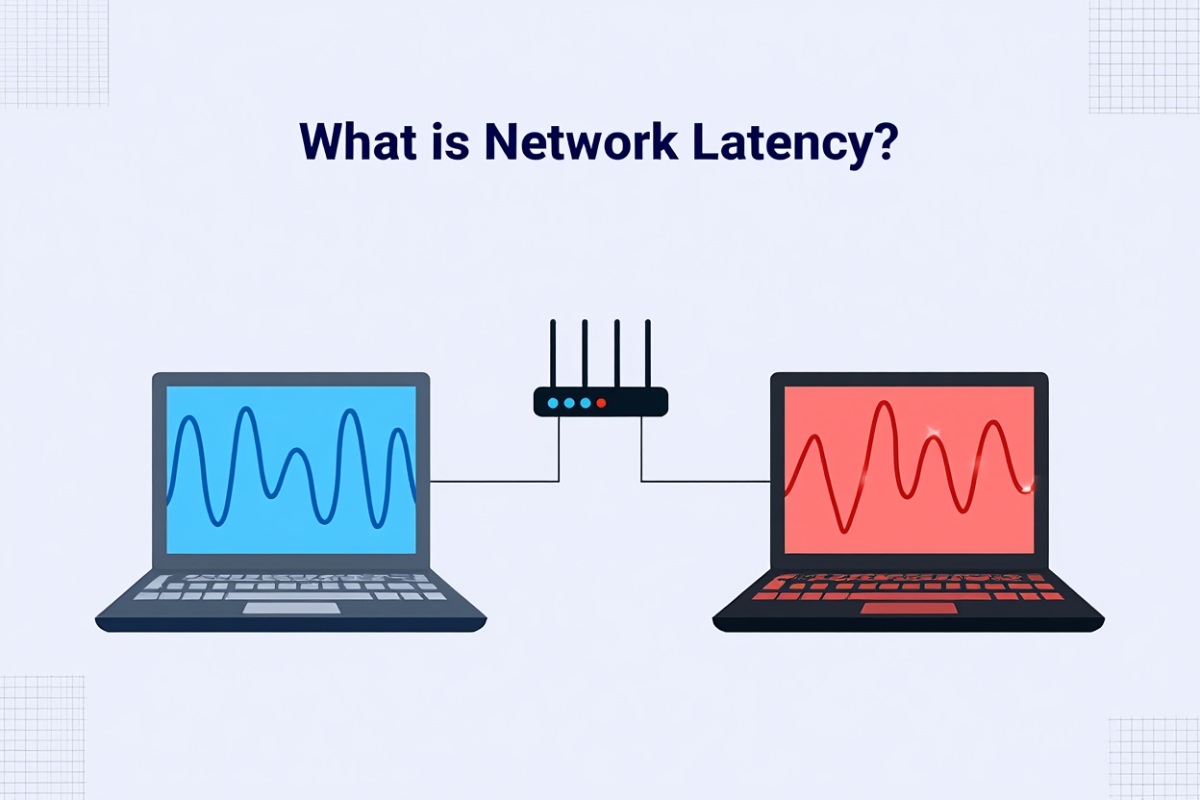
Network latency refers to the time delay between a request for data and the beginning of its delivery across a network. More specifically, it’s the time it takes for a single data packet to travel from its origin (like your device) to its destination (like a web server) and, in many cases, back again.
It’s measured in milliseconds (ms), and even though that sounds minuscule, a difference of just 100 ms can dramatically impact your experience online—especially in activities like gaming, video conferencing, or using cloud apps.
1.1. Latency vs Bandwidth: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse latency with bandwidth, but they are entirely different:
- Bandwidth is how much data can be transferred in a given period (like the width of a highway).
- Latency is how fast one unit of data can get from point A to point B (like how fast a car drives on that highway).1.2. The Round-Trip Journey
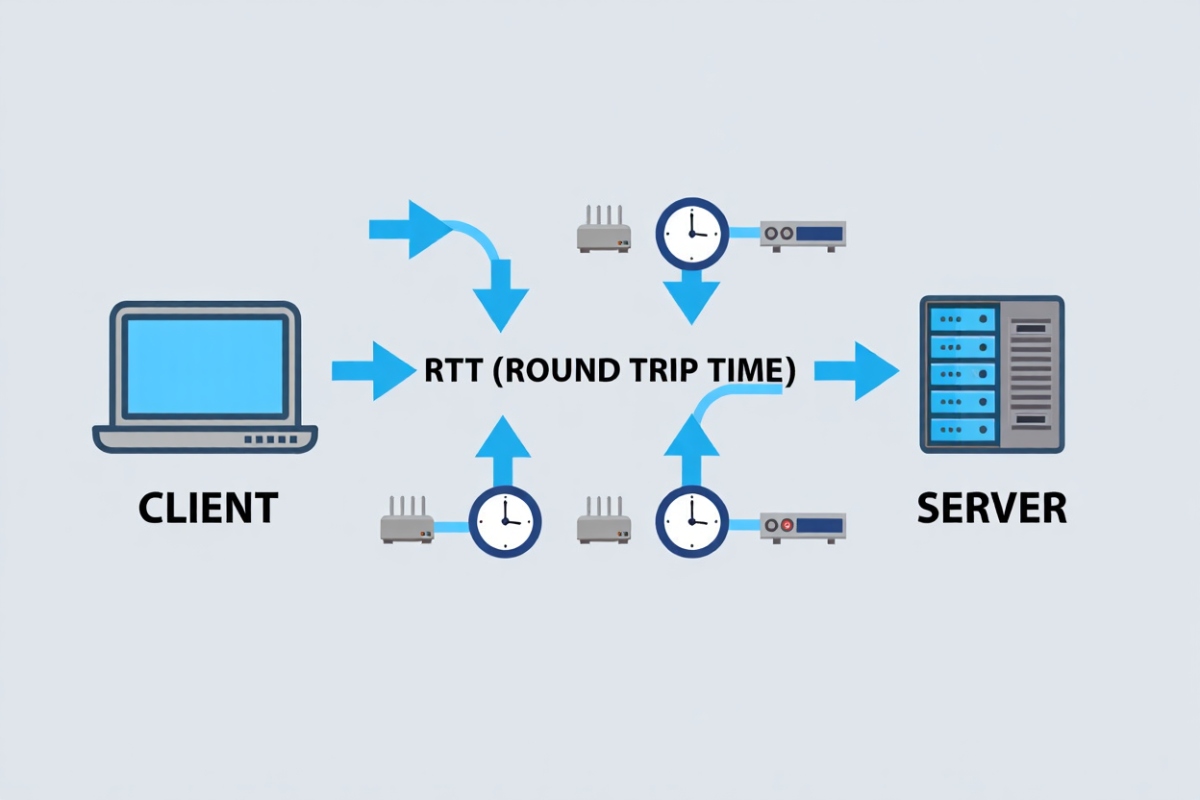
A common way to measure latency is round-trip time (RTT), which includes:
- Time to send a request to a server
- Time for the server to respond
- Total duration = latency
For example, when you click “play” on a YouTube video, your computer sends a request to Google’s servers. The latency is the delay before that video starts playing.
1.3. Why It Matters
High network latency breaks the sense of “real time.” It makes apps feel sluggish, websites slow to respond, and digital collaboration more difficult. On the flip side, low latency means faster feedback, more accurate communication, and a much smoother experience.
Whether you’re a casual internet user or managing systems in finance or healthcare, understanding what network latency is—and how to keep it low—is essential for consistent, high-quality performance.
2. Causes of Network Latency
Network latency isn’t caused by just one issue—it’s often the result of multiple factors working together. Whether you’re on a home Wi-Fi network or managing a business system, understanding these causes is key to identifying and fixing delays.
Dưới đây là các nguyên nhân phổ biến:
2.1. Physical Distance
The farther your data has to travel, the more time it takes to arrive. Even at the speed of light, signals sent from one continent to another experience noticeable delays—especially when multiple data centers and oceanic cables are involved.
2.2. Routing and Number of Network Hops
Each time your data moves from one router or switch to another, it adds a tiny delay. The more “hops” data takes from source to destination, the greater the latency.
- A well-optimized route may take only 5 hops.
- A poorly configured or congested route might require 15+ hops, increasing delay.
2.3. Network Congestion
Just like a highway during rush hour, networks can get congested. Too many data packets trying to move at once causes queuing and delays.
This often happens:
- During peak hours (evenings/weekends)
- In shared office buildings
- In homes where multiple devices stream at the same time
2.4. Hardware and Infrastructure Limitations
Old or overloaded hardware can slow down how quickly data is processed and forwarded. This includes:
- Modems and routers
- Network switches
- ISP infrastructure
If any device along the path isn’t optimized, it becomes a bottleneck that raises latency.
2.5. Wireless Interference
Wi-Fi is convenient, but it’s more susceptible to:
- Signal interference from walls, microwaves, or other wireless networks
- Fluctuating signal strength as you move around
- Packet loss requiring retransmission
These can all add up to higher latency than a wired Ethernet connection.
2.6. Firewalls and Security Software
Firewalls, antivirus programs, and intrusion detection systems often inspect every incoming or outgoing packet. While this adds a security layer, it also introduces delay—especially on underpowered machines or poorly configured firewalls.
2.7. Protocol Inefficiencies
Some older communication protocols are not optimized for speed. For instance:
- TCP requires packet confirmation, which introduces back-and-forth delay.
- UDP is faster but not suitable for all use cases due to lack of reliability.
Depending on the application, choosing the wrong protocol can increase latency unnecessarily.
2.8. Cloud and CDN Routing
If your content isn’t cached close to your location (via Content Delivery Networks), requests might get routed across multiple countries before returning to you.
3. Impact of Network Latency on User Experience
While most people don’t think about milliseconds when using the internet, network latency can drastically change how “fast” or “smooth” something feels online. Even if you have high-speed internet, high latency can make everything seem slower or unresponsive.
Let’s break down how network latency affects real-world digital activities:
3.1. Web Browsing
When you open a website, dozens of small files (images, scripts, stylesheets) need to be requested from a server. If each request is delayed by high latency, the page feels like it’s loading forever—even if your bandwidth is excellent.
3.2. Video Streaming
While streaming platforms like YouTube and Netflix buffer data in advance, latency still plays a role in:
- Startup time (how fast the video begins)
- Resolution adaptation (switching between HD and SD)
- Seeking/scrubbing delay
High latency increases buffer duration, making your viewing experience feel clunky.
3.3. Online Gaming
Gaming is one of the most latency-sensitive activities online. Here, milliseconds matter:
- Latency under 50ms: Smooth gameplay
- 50–100ms: Noticeable lag but playable
- 100ms+: Delayed commands, rubber-banding, and hit registration issues
3.4. Video Conferencing
Tools like Zoom, Google Meet, or Microsoft Teams rely on minimal latency for real-time communication. Even 200ms of delay can result in:
- Talking over one another
- Awkward pauses or echo
- Out-of-sync audio and video
Latency builds up across devices and networks, affecting the natural flow of conversation.
3.5. Cloud-Based Work and SaaS
When using platforms like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, or Figma, every click or action sends a request to the cloud. High latency here results in:
- Slow document saving
- Lag in collaboration tools
- Frustrated users due to non-instant feedback
These issues are especially relevant in the Software as a Service (SaaS) model, where real-time access is essential.
If you’re new to the concept, check out our full beginner-friendly guide on What is SaaS? to understand how cloud-based software works and why latency plays a critical role in user experience.
3.6. Voice-over-IP (VoIP) and Telephony
Just like with video calls, voice services like Skype, WhatsApp, or business VoIP systems demand low latency to avoid:
- Audio delay or echo
- Missing syllables or “robotic” distortion
- Poor call quality
This is especially critical for customer service and call centers.
3.7. Virtual Desktop and Remote Work
In virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) environments, latency directly affects:
- Mouse and keyboard responsiveness
- App load times
- Video playback in a remote session
Employees using remote desktops over long distances suffer more if latency isn’t managed.
3.8. IoT Devices and Automation Systems
For industrial IoT or smart home setups:
- Sensors may not report real-time data
- Automated systems (e.g., smart locks or thermostats) respond slower
- Latency can even be a safety concern in robotics or healthcare settings
4. Measuring Network Latency
Before you can fix latency issues, you need to measure them. Fortunately, several built-in tools and third-party applications make it easy to check how much delay your network is experiencing—and where that delay is coming from.
Let’s explore the most effective methods to measure network latency, even if you’re not a network expert.
4.1. Using the Ping Command
The ping tool is the simplest and most widely used method to test latency.
- It sends a small packet (called an ICMP echo request) to a server.
- The server responds with an echo reply.
- The time between sending and receiving is your round-trip time (RTT).
How to use:
- On Windows: Open Command Prompt →
ping google.com - On macOS/Linux: Open Terminal →
ping google.com
What you’ll see:
Reply from 142.250.190.78: bytes=32 time=24ms TTL=118
Here, time=24ms is the latency.
4.2. Using Traceroute (tracert)
Traceroute (or tracert on Windows) maps the path your data takes to reach its destination and shows the latency at each hop along the way.
How to use:
- On Windows:
tracert google.com - On macOS/Linux:
traceroute google.com
This reveals:
- Number of hops between your device and the server
- Delay introduced at each step
- Where major slowdowns occur
4.3. Speed Test Websites
Websites like Speedtest.net or Fast.com include latency measurements, usually labeled as:
- Ping: round-trip delay to their test server
- Jitter: variation in latency (inconsistent delay)
These tools are great for quick checks, especially when troubleshooting gaming or video call issues.
4.4. Network Monitoring Tools
For deeper analysis, especially in business or IT environments, you can use tools like:
- Wireshark – packet capture and inspection
- SolarWinds Pingdom – real-time latency monitoring for websites
- Nagios or Zabbix – network-wide latency and performance graphs
These tools provide:
- Historical data over days/weeks
- Alerts when latency exceeds thresholds
- Breakdown of application vs network delay
4.5. Mobile Apps for On-the-Go Testing
Apps like PingTools, Net Analyzer, or Fing allow you to measure latency from smartphones or tablets—useful for diagnosing Wi-Fi issues or comparing mobile vs wired performance.
4.6. When Is Latency a Problem?
Here’s a simple reference guide:
| Latency (ms) | Performance Rating |
|---|---|
| 0–20 ms | Excellent (ideal for gaming, VoIP) |
| 20–50 ms | Good (most uses feel real-time) |
| 50–100 ms | Fair (acceptable but noticeable) |
| 100–200 ms | Poor (lags, delays, buffering) |
| 200+ ms | Unusable for real-time apps |
By measuring network latency regularly, you can pinpoint slowdowns, verify improvements after changes, and better communicate with ISPs or IT support.
5. Strategies to Reduce Network Latency
Now that you’ve identified what network latency is and what causes it, the next logical step is to learn how to reduce it. Whether you’re a casual user, a gamer, or a network administrator, these practical strategies will help lower latency and improve your online experience.
5.1. Switch to Wired Connections (Ethernet)
Wireless connections are convenient, but they often introduce interference and additional processing delays. A direct Ethernet cable connection is more stable, consistent, and usually offers significantly lower latency.
5.2. Use Local Servers or CDNs
If you’re accessing content or services hosted far away, you’ll experience higher latency due to distance. To reduce this:
- Choose apps/services that use local servers
- If you run a website or app, implement a Content Delivery Network (CDN) like Cloudflare or Akamai
- Use geo-targeted DNS or hosting if possible
5.3. Optimize Router and Network Hardware
Outdated or overloaded routers/switches can bottleneck your traffic. Upgrade to:
- Modern routers with low-latency processing
- Gigabit switches
- Devices with QoS (Quality of Service) features to prioritize real-time traffic like VoIP and gaming
Don’t forget to:
- Reboot routers periodically
- Place them in central, interference-free locations
- Keep firmware up to date
5.4. Enable Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS settings on a router let you assign priority to certain types of traffic, such as:
- Voice calls
- Video conferencing
- Online games
This ensures that high-priority traffic isn’t delayed by background activities like downloads or streaming.
5.5. Reduce Background Bandwidth Usage
Applications like cloud backups, automatic updates, and idle streaming tabs can consume bandwidth and increase latency.
Actionable tips:
- Close unused browser tabs and applications
- Pause or schedule large file uploads/downloads
- Use bandwidth monitoring tools to detect silent data usage
5.6. Minimize Network Hops
Each router or switch between you and the destination adds delay. While some hops are unavoidable, you can:
- Use VPNs with optimized routes (e.g., for gaming)
- Choose ISPs with better peering relationships
- Avoid daisy-chaining multiple network extenders
5.7. Regularly Scan and Secure Your Network
Malware, misconfigured firewalls, or unauthorized users on your network can slow things down.
- Use antivirus software and scan for threats
- Secure Wi-Fi with strong passwords
- Block unknown devices from your router admin panel
Read more:
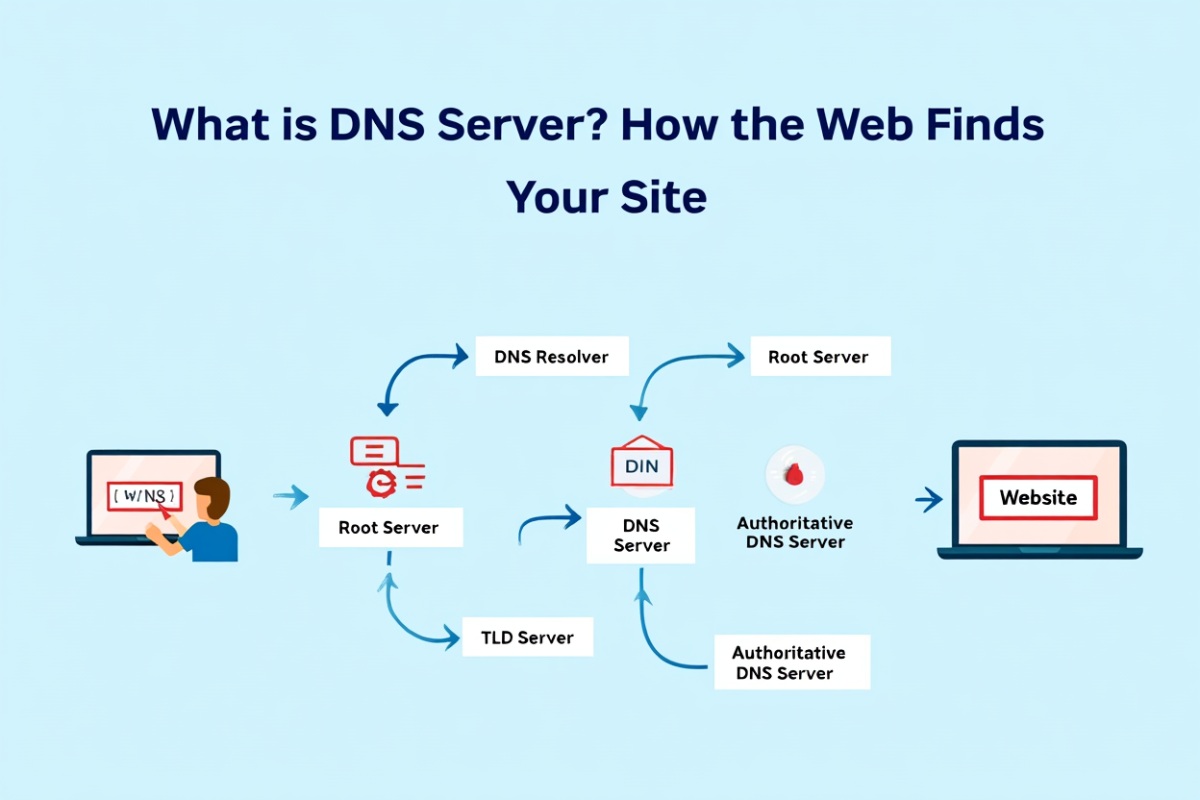
- What Is DNS Server? The Internet Shortcut You Never Knew You Needed
- What Is a VPN? A Complete Beginner’s Guide to Online Security
- What is LAN vs WAN? Key Differences Explained for Everyday Users
- What is Subnet Mask? A Beginner-Friendly Guide to IP Networks
- What Is a Firewall? A Comprehensive Guide to Network Security
6. Real-World Applications and Considerations
Network latency isn’t just a technical term for IT professionals—it impacts every corner of our connected world. Whether it’s financial systems executing trades in milliseconds or a doctor performing remote surgery, reducing latency is essential for both performance and safety.
Here are some real-world applications where latency plays a critical role:
6.1. Online Gaming
In fast-paced games like FPS (first-person shooters) or MOBAs, low latency is critical for:
- Instant response time
- Accurate hit registration
- Competitive advantage
6.2. Video Conferencing and Remote Work
Apps like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet need consistent low latency for real-time conversation. Delays over 150ms can lead to:
- Talking over each other
- Video-audio desync
- Frustration and lost productivity
Remote desktop users in VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) environments are especially affected by even slight delays.
6.3. E-Commerce and Web Apps
Latency affects conversion. Studies show:
- Pages that load in under 2 seconds have the highest conversion rates.
- Every 100ms of delay can reduce customer satisfaction and increase bounce rates.
6.4. Telemedicine and Healthcare
In remote diagnostics or live surgery assistance, even a 200ms delay can result in:
- Miscommunication
- Mistimed instrument control
- Increased risk to patient safety
Hospitals now invest in private fiber links or edge computing to reduce medical latency.
6.5. Financial Trading Systems
High-frequency trading platforms rely on ultra-low latency to execute market orders faster than competitors. Just 1ms advantage can be worth millions.
Firms co-locate servers in data centers near exchanges and use specialized fiber optics to gain milliseconds.
6.6. Industrial IoT and Automation
Smart factories and automated warehouses use sensors, robotic arms, and machine-to-machine communication that demand <10ms latency for:
- Real-time production adjustments
- Fault detection
- Worker safety
6.7. Education and E-Learning
Live streaming lessons, remote whiteboards, and collaborative tools require low latency so students and instructors can interact smoothly—especially with global students.
Delays can cause miscommunication and loss of engagement.
7. Conclusion
So, what is network latency? It’s the time delay in digital communication—and it affects almost everything we do online. From video calls to online shopping, every extra millisecond counts.
By understanding the causes of latency and applying practical fixes, you can make your internet feel faster and your online experience smoother.
For more practical guides like this, visit the Networking section at Softbuzz. Got questions or want help reducing your network delays? Drop a comment—we’re happy to help!