What is NFC on Android? It’s a short-range wireless technology that allows your phone to interact with nearby devices—within 4 cm—without needing Wi-Fi or mobile data. Common uses include tap-to-pay, file sharing, fast Bluetooth pairing, and smart home automation.
I still remember the first time I tapped my Android phone to pay for a coffee—it felt like magic. In 2025, NFC on Android has become a quiet assistant in my daily life, helping me unlock doors, pair earbuds, and automate routines—all with a simple tap.
This guide will show you what NFC is, how it works, and how to use it to simplify your everyday tasks securely and efficiently.
What is NFC on Android?
NFC (Near Field Communication) is a short-range wireless technology that enables Android smartphones to exchange data within a few centimeters—typically under 4 cm. Evolving from RFID, NFC allows instant communication without needing power or internet when interacting with NFC tags.
I still remember the first time I tapped my Android phone to pay for a coffee—it felt futuristic. Today, NFC is something I use daily: unlocking my front door, connecting my earbuds, sharing contact info, or automating my smart home, all with a simple tap.
Core Features of NFC on Android (With Real-Life Examples)
1. Ultra-Short Range (≤4 cm)
The close proximity enhances security and ensures intentional interactions.
I use it to pay at metro gates or checkout counters—no PIN, no cards, just a tap.
2. Built-in Support Across Android Devices
Most Android phones (Android 9 and up) come with NFC chips, allowing users to access contactless payments, quick pairing, and data transfers.
Even budget models like the Pixel 6a now include NFC as standard.
3. Zero Setup Required
No need for pairing or network setup.
For instance, I often share my home Wi-Fi by tapping phones together—no password needed.
4. Complementary to Other Wireless Tech
NFC doesn’t replace Bluetooth or Wi-Fi—it works alongside them for tasks they can’t handle efficiently, such as one-tap identity verification or ticket validation.
NFC vs Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi vs QR Code: A Practical Comparison
| Feature | NFC | Bluetooth | Wi-Fi | QR Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | ≤ 4 cm | Up to 10 meters | Up to 100 meters | Requires camera & scan |
| Setup | Instant | Requires pairing | Needs configuration | Needs manual scanning |
| Best Use | Tap-to-pay, automation | Audio devices | Internet access | Accessing links/info |
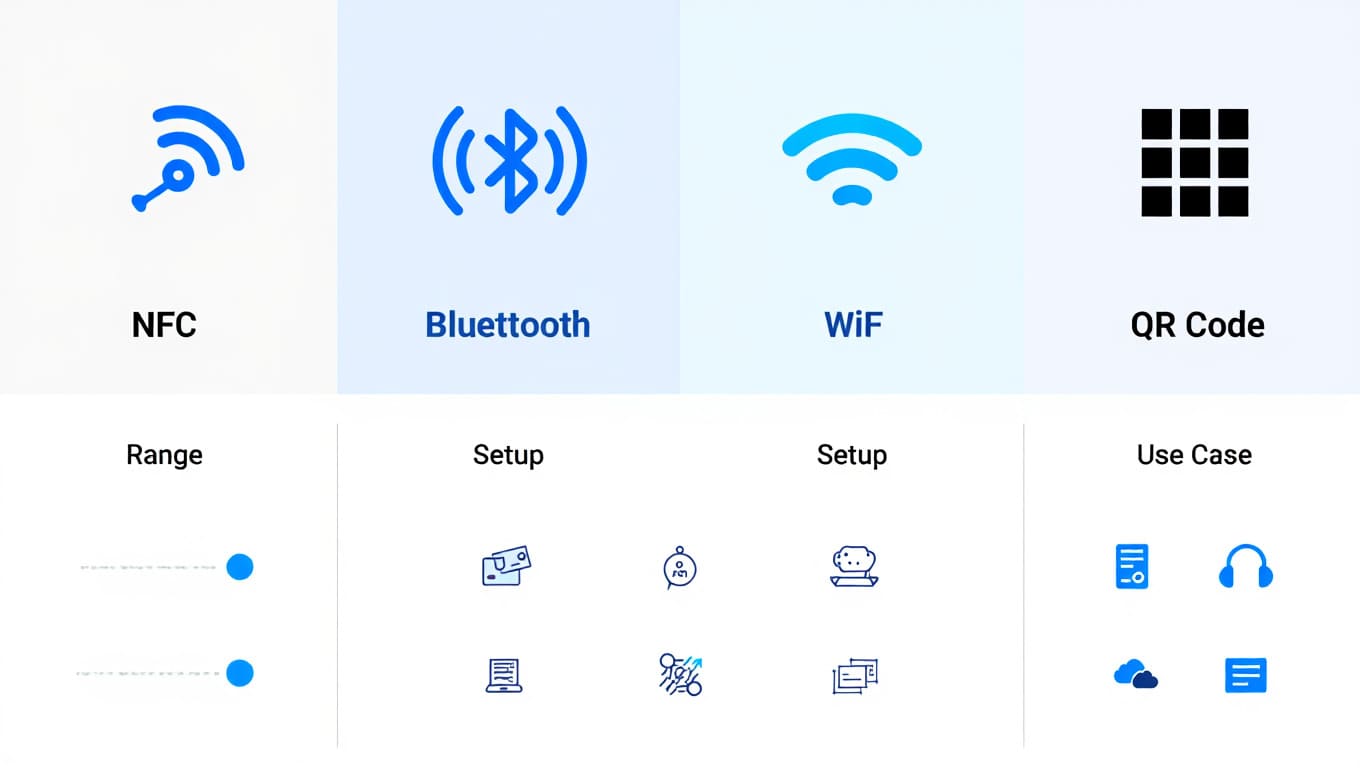
NFC vs Other Wireless Technologies
In short, NFC excels in quick, secure, and low-effort interactions, making it ideal for everyday tasks that require immediacy. Personally, it’s one of the most underrated yet powerful tools on any Android phone.
How Does NFC Work on Android Devices?
At its core, NFC on Android uses a small chip and antenna inside the phone to generate a magnetic field. When your phone comes within a few centimeters of another NFC-enabled device or a tag, this field activates communication instantly—no Wi-Fi, mobile data, or even power on the tag is needed.
Reader/Writer Mode
In this mode, your phone reads or writes data to passive NFC tags, which are common in smart posters, museum exhibits, or home automation setups.
For example, I have a tag at my bedside—tapping it automatically puts my phone in Do Not Disturb mode and dims the lights.
Card Emulation Mode
Here, your Android device acts like a contactless card—this is how Google Pay works. It uses secure elements or Host Card Emulation (HCE) to transmit encrypted payment data to point-of-sale terminals.
Every time I pay for coffee with a tap, this mode ensures my real card number stays protected.
Peer-to-Peer Mode
This lets two devices exchange small files or data—like sharing contacts, photos, or URLs—without needing to pair or connect to a network.
I once used this at a tech event to instantly swap contact details with another attendee by just tapping our phones together.
What Can You Do with NFC on Android?
NFC on Android isn’t just for flashy payments—it’s a powerful, underused feature that can streamline your daily routines, improve security, and unlock personalized automation. Here are the most practical and impressive ways NFC can transform how you use your Android device:

NFC in Daily Life
1. Contactless Payments and Transactions
Use Cases:
-
Make secure payments at stores, restaurants, or metro stations with Google Pay or Samsung Pay.
-
Tap your phone to vending machines, buses, or POS terminals to pay instantly—no need to carry cards or cash.
Example: I tap my phone at the train station every morning—it’s faster than using my physical transit card and tracks all my rides automatically.
2. Instant Device Pairing
Use Cases:
-
Pair Bluetooth headphones or smart speakers by simply tapping your Android phone.
-
Quickly connect to Wi-Fi routers or smart home hubs with pre-configured NFC tags.
Why It Matters: No more navigating settings or entering passwords—just tap and connect.
3. NFC Tag Automation
Use Cases:
-
Program tags to trigger daily routines: enable silent mode, open a playlist, or launch Google Maps.
-
Use them in your car, bedroom, office, or entryway.
Example: John placed a tag by his bed—each morning, tapping it disables Do Not Disturb, opens a news app, and starts Spotify.

NFC Tag Use at Night
4. Business Cards and Event Check-ins
Use Cases:
-
Instantly share your professional contact details with a tap.
-
Tap your phone to check in at conferences, events, or secure buildings using NFC-enabled tickets or badges.
Pro Tip: NFC business cards leave a strong impression—no more running out of paper cards.
5. File and Contact Sharing
Use Cases:
-
Share photos, contacts, documents, or app links between Android devices with just a tap.
-
Ideal for fast, cable-free transfers in meetings or social gatherings.
Note: While Android Beam is deprecated, third-party apps like “NFC Tools” enable this functionality.
6. Smart Home & IoT Integration
Use Cases:
-
Control smart lights, thermostats, or door locks by tapping a wall-mounted NFC tag.
-
Send documents to NFC-enabled printers without logging into any system. And to make your digital life even more seamless, pairing NFC routines with cloud backup ensures your files and smart device data are always safe—automated and accessible anytime.
Example: I stuck an NFC tag at the front door—tapping it activates the security camera and locks all doors.
7. Access Control and Authentication
Use Cases:
-
Enter office buildings, hotel rooms, or coworking spaces without keys—just use your phone.
-
Authenticate your identity for government services or secure apps using NFC ID tokens.
Security Note: Most systems use encrypted protocols to protect your credentials.
8. Parental Controls and App Triggers
Use Cases:
-
Restrict app access or launch child-safe content when a tag is scanned.
-
Perfect for managing screen time or switching to learning apps with a simple tap.
Parent Hack: Place an NFC tag on a tablet that launches a pre-approved app list.
9. Healthcare Access and Smart Info Points
Use Cases:
-
Healthcare professionals can scan patient wristbands to access medical history securely.
-
Shoppers can scan product labels for nutritional info, expiry dates, or allergens.
Example: Some pharmacies now offer NFC-enabled medicine boxes—scan to get dosage reminders and refill alerts.
These real-world NFC use cases show that your Android phone can do far more than you imagined—automating tasks, increasing security, and reducing friction in your daily life.
How to Check, Enable, and Use NFC on Your Android Phone
Wondering if your Android phone supports NFC and how to make the most of it? Whether you’re setting up contactless payments or automating routines with NFC tags, follow this guide to check, enable, and use NFC like a pro.
Step 1: Check If Your Android Device Has NFC
Method 1 – Use Settings Search:
-
Open Settings
-
Tap Connected Devices > Connection Preferences
-
Look for the NFC toggle
-
If found, your device supports NFC.
Method 2 – Search Bar:
-
Type “NFC” in the Settings search bar
-
If nothing shows up, check your model’s specs on the manufacturer’s website.
Author Tip:
I once bought a budget Android phone only to realize NFC wasn’t supported—always check specs before purchasing if this feature matters to you.
Step 2: Enable NFC Functionality
Generic Android:
-
Go to Settings > Connected Devices > NFC
-
Toggle NFC to ON
Samsung Devices:
-
Go to Settings > Connections > NFC and Payment
-
Toggle it ON and set your default payment method
Google Pixel Devices:
-
Go to Settings > Connected Devices > Connection Preferences > NFC
Step 3: Set Up a Default Tap-to-Pay App
-
Navigate to Settings > Tap & Pay or Contactless Payments
-
Choose Google Pay, Samsung Pay, or other apps as your default service
Pro Tip:
Google Pay is widely accepted and easy to set up—it’s my go-to for daily transit and coffee shop purchases.
Step 4: Use NFC to Read and Write Tags
-
Reading Tags: Tap your phone against an NFC tag to open a link, play media, or show a message.
-
Writing Tags: Download apps like NFC Tools to encode tags with custom actions—Wi-Fi login, open apps, trigger automation.
Example Use:
I have a tag near my work desk. A single tap connects my phone to Wi-Fi, turns off notifications, and opens Slack.
Step 5: Use NFC to Pair Devices Instantly
-
Make sure Bluetooth is enabled
-
Tap your Android phone to an NFC-enabled Bluetooth speaker, printer, or earbuds
-
No need for PINs or pairing screens—just tap and connect
By following these steps, you’ll unlock NFC’s full potential—whether it’s contactless payments, automating your daily routine, or sharing data with a tap.
Is NFC Safe? Security & Privacy on Android
NFC on Android is designed with security at its core, thanks to its short-range operation (under 4 cm) and robust encryption protocols—especially in payment and identity verification scenarios. For even stronger mobile privacy, many users also combine NFC with VPN services to protect their data across all apps and networks.
Android phones utilize hardware-backed components like the Secure Element (SE) or rely on Host Card Emulation (HCE) combined with dynamic tokenization to protect sensitive data such as credit card numbers during transactions. This ensures that your data is encrypted, anonymized, and never stored or transmitted in plain form.
Additionally, Android enforces strict app permission controls, allowing only apps with explicit NFC permissions to interact with the NFC hardware—minimizing unauthorized access.

Common NFC Myths Debunked
Myth 1: Someone can steal my credit card info by just standing nearby.
Fact: NFC requires active, intentional proximity—usually less than 4 cm—and often user authentication (e.g., fingerprint, PIN). Passive scanning without contact is virtually impossible.
Myth 2: NFC constantly tracks my location.
Fact: NFC does not transmit location data. It only activates when near another NFC-enabled object and does not “broadcast” in the background.
Myth 3: NFC is easier to hack than Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
Fact: On the contrary, NFC’s limited range and lack of persistent connectivity make it less vulnerable to remote hacking than other wireless technologies.
Best Practices to Use NFC Securely
-
Turn off NFC when you’re not using it—this reduces exposure to unnecessary scans.
-
Use only trusted apps like Google Pay or Samsung Pay for transactions.
-
Review app permissions regularly and uninstall apps that request unnecessary access.
-
Avoid scanning unknown tags in public places—just like clicking random links online, rogue tags can trigger unwanted actions.
-
Keep your phone’s OS and payment apps updated to ensure the latest security patches are in place.
Advanced NFC Features for Power Users & Developers
For enthusiasts and developers, Android offers advanced NFC capabilities via APIs such as NDEF (NFC Data Exchange Format), Foreground Dispatch allowing apps to prioritize NFC events, and Host Card Emulation (HCE) for creating virtual cards or secure transactions without physical Secure Elements.
Developers can build custom apps to program complex NFC tag workflows, integrate NFC with smart home automation platforms, or develop secure authentication systems tailored to business or educational environments.
Notable examples include access management systems for enterprises, automated attendance tracking in schools, and contactless patient data retrieval in healthcare settings. Google’s Android Developer website provides comprehensive documentation and code samples to explore these possibilities.
Troubleshooting: Why Isn’t NFC Working on My Android?
If you’re facing NFC issues on your Android phone, here’s how to diagnose and resolve them:
1. Device Compatibility:
Not all Android phones support NFC. Check your phone specs or use the Settings search bar to confirm.
2. NFC Disabled:
Go to Settings > Connected Devices > Connection Preferences > NFC and ensure it’s toggled ON.
3. Battery Saver Mode:
Power-saving modes may restrict background NFC functionality—disable them during use.
4. Interference from Cases or Stickers:
Thick, metal, or magnetic cases may block the antenna. Try removing the case and scanning again.
5. Software or App Glitches:
-
Clear the cache for your payment or NFC-related apps
-
Reboot your device
-
Update Android system and payment apps
6. Payment or Tag Fails:
-
Test with a known working NFC tag
-
Check payment compatibility with your bank or region
-
Ensure your account/card is active and not blocked
Advanced NFC Features for Power Users & Developers
Beyond simple payments or tag reading, Android offers developers and power users a full suite of advanced NFC functionalities:
Key Capabilities:
-
NDEF (NFC Data Exchange Format): Enables structured data storage and transfer.
-
Foreground Dispatch System: Prioritize specific NFC interactions in your app.
-
Host Card Emulation (HCE): Create virtual payment cards or badges without requiring physical secure hardware.
Real-World Applications:
-
Enterprise-level access control (e.g., badge-based entry)
-
Classroom attendance tracking using NFC ID cards
-
Hospital patient wristbands for real-time data access
-
Smart poster marketing that launches product pages upon tap
Resources:
Google’s Android Developer NFC Guide includes extensive documentation and sample code for building secure, NFC-enabled Android apps.
By understanding how Android safeguards NFC and applying a few smart habits, you can enjoy the speed and convenience of tap-based interactions without compromising on privacy or security.
Supplemental: 30+ NFC Questions & Answers for Android Users (FAQ)
Got questions about how NFC works on your Android phone? Here’s a curated, easy-to-scan FAQ covering everything from security and battery usage to automation and real-world applications.
NFC Basics
What does NFC mean on my phone?
NFC stands for Near Field Communication, a wireless technology enabling devices to exchange data when in very close proximity (under 4 cm).
Does every Android phone have NFC?
No. While most modern mid-range and flagship Android phones do, some budget models and older devices lack built-in NFC hardware.
How close do devices need to be for NFC to work?
Within 4 centimeters. This close-range requirement enhances both security and accuracy.
Is NFC faster than Bluetooth?
Yes—for connection initiation. NFC connects instantly, whereas Bluetooth requires pairing steps and longer setup.
What’s the difference between NFC and Bluetooth?
NFC is best for short-range, quick interactions like payments or tag scans. Bluetooth supports longer-range, continuous connections like audio streaming.
NFC Security & Privacy
Can NFC be hacked?
While no wireless tech is 100% invulnerable, NFC is very secure thanks to its short range and encrypted communication, especially for payments.
Is contactless payment safe?
Yes. NFC payments use tokenization, encryption, and hardware-backed security like the Secure Element or HCE (Host Card Emulation).
Does NFC track my location?
No. NFC only activates when two devices are close and does not track or broadcast your location.
Is NFC safer than QR codes?
Generally yes. NFC relies on proximity-based activation and encrypted channels, while QR codes can be spoofed or misused via phishing.
Are there health risks with NFC?
No. NFC uses low-frequency, low-power radio waves similar to Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, posing no known health risks.
Glossary & Supplemental Tables
- NFC (Near Field Communication): A wireless technology enabling short-distance data exchange.
- NDEF (NFC Data Exchange Format): Standard format for storing data on NFC tags and devices.
- HCE (Host Card Emulation): A technology allowing phones to emulate smart cards for payments and access without a secure element.
- Secure Element: A tamper-resistant chip that safely stores sensitive data such as payment credentials.
- Tag: A passive NFC device that holds data readable by NFC-enabled phones.
- Peer-to-Peer: Mode allowing two NFC devices to exchange data mutually.
Popular NFC Android Phones (2020–2025):
- Samsung Galaxy S21–S23 series
- Google Pixel 5–8 series
- OnePlus 8T and newer
- Samsung Galaxy A series mid-range phones
- Motorola Moto G series (selected models)
Each model integrates NFC differently; check specific specs for antenna placement and feature variations.
Performance & Power Usage
Will NFC drain my battery?
Very little. When idle, NFC uses negligible power, and even when active, the impact is minimal.
Does NFC work with the screen off?
Yes, on many Android devices—especially for payments or tag reading—though this may vary by model or setting.
Does NFC require the internet to work?
No. NFC itself works offline, but specific apps (e.g., payments) may require an internet connection for processing.
NFC for Payments & Identification
Do I need a SIM card for NFC payments?
No. As long as your phone supports NFC and has a configured payment app (like Google Pay), SIM is not required.
Can NFC replace my access badge or key?
Yes. Many office buildings, hotels, and smart locks support NFC-based authentication via smartphones.
Can I use NFC abroad?
Yes. NFC is a global standard, but local support depends on whether payment terminals or services accept NFC.
What should I do if my bank doesn’t support NFC?
Try alternate apps like Samsung Pay, Google Wallet, or your bank’s mobile app, or use a physical card as a backup.
Can NFC be used for ticketing?
Yes. Public transit systems, concerts, and events often use NFC for digital tickets and contactless check-in.
sing & Managing NFC
How can I automate my home with NFC?
Program NFC tags to trigger smart home actions using apps like NFC Tools, Trigger, or SmartThings.
Can NFC trigger actions automatically?
Yes. NFC tags can launch apps, toggle settings, or initiate sequences like connecting to Wi-Fi or playing music.
Can I program NFC tags with my phone?
Yes. Most Android phones support writing to tags via apps like NFC Tools or TagWriter by NXP.
How do I erase or format an NFC tag?
Use your NFC writing app to format, erase, or overwrite the tag content.
Can I disable or restrict NFC apps?
Yes. Go to Settings > Apps and manage permissions for any app that uses NFC. You can also uninstall unused apps.
Device Compatibility & Technical Info
Can I use NFC with cases?
Thin cases usually don’t interfere. However, metal or magnetic cases may block the NFC signal.
Is NFC available on older Android phones?
Some older flagship phones support NFC, but check the specs for confirmation.
How are NFC tags powered?
Passive tags draw energy from the electromagnetic field emitted by your phone—no battery needed.
Can NFC connect to printers or other devices?
Yes, some printers and devices support tap-to-pair via NFC for quick configuration.
Is there a list of Android phones with NFC?
Yes. Sites like GSMArena, AndroidAuthority, and XDA publish updated lists of NFC-capable phones.
Can I turn off NFC notifications?
Most Android phones let you manage NFC alerts and sounds via the Settings > Notifications menu.
Developer & Power User Features
What advanced features does NFC offer developers?
-
NDEF (NFC Data Exchange Format)
-
Host Card Emulation (HCE)
-
Foreground Dispatch System for app-specific tag handling
Real-World Developer Use Cases:
-
Contactless patient info retrieval in hospitals
-
School attendance systems with NFC ID badges
-
Secure access control apps for enterprises
Where can I learn to build NFC apps?
Visit Android Developer – NFC Guide for documentation, code samples, and API references.
Conclusion
NFC on Android has matured into a versatile, secure, and user-friendly technology that powers countless everyday interactions—from effortless mobile payments and Bluetooth device pairing to smart automation and secure access control. Understanding what NFC is on Android, how it functions, and how to use it effectively allows users to unlock its full potential.
By following basic setup instructions and adhering to proven security practices, Android users can confidently integrate NFC into their digital routines. For power users and developers, NFC also provides advanced opportunities—fueling innovation in smart home systems, contactless business tools, and beyond.
As Android evolves in 2025, NFC continues to bridge the physical and digital worlds with unmatched speed and security.
Want to explore more Android features like NFC? Visit our Mobile section for in-depth guides, tips, and tutorials.
For the latest in mobile tech, apps, and smart solutions, head over to the Softbuzz and stay connected to what’s next.










