What is Windows Task Manager? It’s the first thing I turned to when my laptop fan roared like a jet and apps started lagging for no reason. With a few clicks, I spotted a background process eating up 98% of my CPU. Ending that task brought my system back to life—without a restart, without panic.
Windows Task Manager is a built-in system utility that shows you everything happening under the hood: running apps, CPU usage, RAM consumption, disk activity, and more. Whether you’re closing a frozen app or analyzing why your system feels sluggish, this tool gives you clarity—and control.
In this complete 2025 guide, we’ll answer the question “What is Windows Task Manager” in depth:
- What each tab does
- How to use it for troubleshooting
- Why it’s essential for keeping your PC healthy and secure
Whether you’re a curious Windows user or a seasoned IT pro, mastering Windows Task Manager is one of the smartest moves you can make.
What is Windows Task Manager?
Windows Task Manager is a system monitoring application that provides a real-time overview of your computer’s processes, performance, and resource usage. It enables users to track applications, background processes, and system services, giving insight into CPU, memory, disk, and network utilization. Beyond monitoring, Task Manager lets you take action—whether ending an unresponsive app, adjusting startup programs, or diagnosing performance bottlenecks.
Key functions include:
- Viewing and managing currently running apps and background processes
- Monitoring detailed system performance metrics such as CPU, RAM, disk usage, and network activity
- Controlling which programs launch at startup to optimize boot times
- Accessing detailed information about user sessions and system services
- Diagnosing and resolving software-related issues that can cause freezes or slowdowns
For example, if a program stops responding, you can open Task Manager, locate the frozen app under the Processes tab, and click “End Task” to close it safely. This practical function highlights why Task Manager is a frontline defense against system instability and sluggishness.
Why is Task Manager Important ?
Task Manager plays a crucial role in maintaining system health, boosting productivity, and ensuring security on Windows PCs. By providing visibility into running applications and system resource consumption, it empowers users to quickly troubleshoot problems and improve efficiency.
- Security: Identify suspicious or unknown processes that could indicate malware.
- Efficiency: Close unresponsive programs consuming excessive memory or CPU, restoring normal operation.
- Diagnostics: Monitor resource usage trends to detect underlying causes of system slowdowns.
- Accessibility: Easily accessed by beginners and IT pros alike, fitting home computing and enterprise environments.
For instance, an IT administrator might use Task Manager to remotely determine why a workstation is slow and identify resource-heavy applications that need optimization or removal.
How to Open Windows Task Manager
Accessing Task Manager is straightforward with multiple methods to fit different user preferences and scenarios. Here are the primary ways:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc for direct access to Task Manager.

- Use Ctrl + Alt + Delete, then select Task Manager from the menu.

- Right-click the Taskbar and choose “Task Manager” from the context menu.

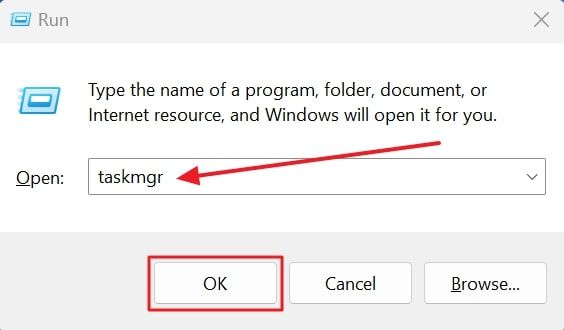
- Open the Run dialog (Windows Key + R), type taskmgr.exe, and press Enter.
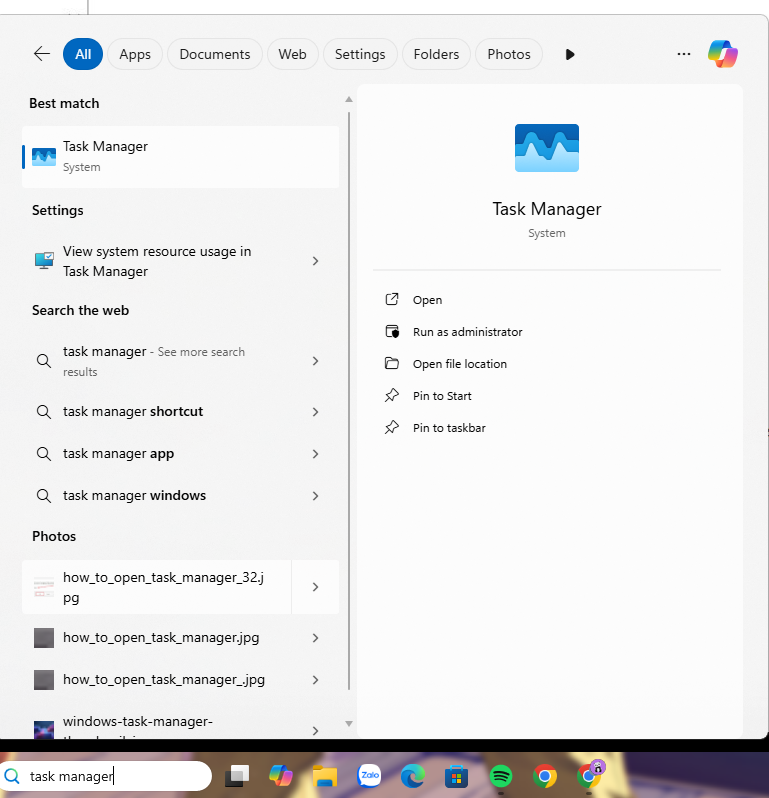
- Use Windows Search by typing “Task Manager” and selecting the app.
If keyboard shortcuts don’t work, ensure your system isn’t locked by group policy restricting access. Alternatively, rebooting or running an antivirus scan may resolve underlying issues preventing Task Manager from opening.
Navigating the Task Manager Interface
Task Manager offers two main interface modes: a simple, compact view and a detailed expanded view. The simple view displays only running applications, ideal for quick checks. Clicking “More details” expands the window, revealing additional tabs and in-depth information. Key interface elements include:
- Processes: Lists running applications and background tasks with current CPU, memory, disk, and network usage.
- Performance: Real-time resource graphs for CPU, memory, disk, and network.
- App history: Tracks resource usage by UWP (Universal Windows Platform) apps over time.
- Startup: Manage programs that launch when Windows boots.
- Users: View user sessions and their resource consumption.
- Details: Provides granular process information including PID, status, and resource metrics.
- Services: Lists background services and lets you start or stop them.

You can resize the window, customize columns via right-click, and use context menus for quick actions like “End task” or “Open file location.” Upon opening, the Processes tab is usually what users see first to start monitoring.
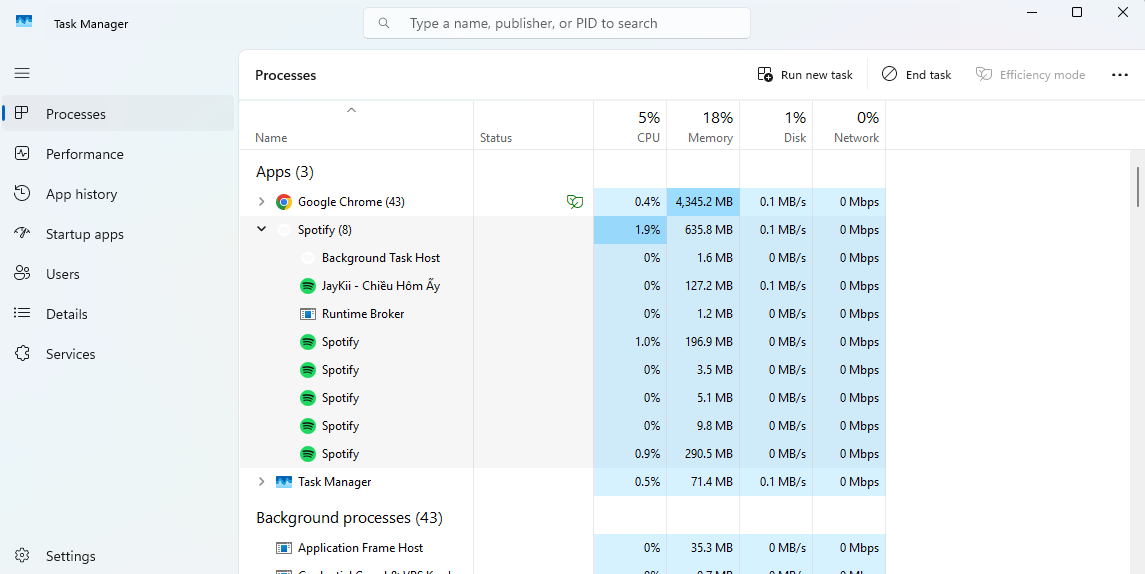
Processes Tab
To truly understand What is Windows Task Manager, it’s crucial to start with the Processes tab is one of the most-used features in Windows Task Manager, offering a live view of every application, background process, and system service running on your PC. Each entry is categorized and displays real-time metrics such as CPU, Memory, Disk, Network, and GPU usage—making it easy to identify what’s slowing your system down.
Here’s how to make the most of it:
- End unresponsive apps: Right-click a frozen or high-resource app and select “End task” to free up system resources instantly.
- View process details: See whether a process is an application or a background service, along with its current load on your system.
- Monitor by user: In multi-user setups, track which user session is consuming the most resources.
For example, if your PC is suddenly slow, opening the Processes tab in Windows Task Manager might reveal that a browser tab is eating up 90% of your memory. Ending just that tab can restore full speed—without restarting the system.
Advanced tip: Right-click any suspicious or unresponsive process and choose “Analyze wait chain” to diagnose thread deadlocks, which are often hidden causes of app freezes.
Understanding how to use the Processes tab is a major step in mastering what Windows Task Manager is truly capable of—helping you troubleshoot issues in real time and maintain a stable Windows environment.
Performance Tab
The Performance tab in Windows Task Manager gives you a high-level, real-time snapshot of your system’s hardware usage—CPU, memory (RAM), disk, network, and GPU. This section is where you see the heartbeat of your PC, visualized through clean, dynamic charts.
These visuals highlight usage patterns, speeds, and capacity, enabling users to spot performance bottlenecks or hardware issues. A spike in CPU or memory usage could signal an app crash or lead to system instability—and in worst cases, even trigger a blue screen of death (BSOD) if left unchecked.
Key metrics tracked in this tab include:
- CPU usage (percentage, speed, number of cores/threads in use)
- Memory stats: available vs used RAM, cached memory, paging file usage
- Disk read/write speeds and activity time
- Ethernet or Wi-Fi throughput: upload/download rates, adapter names
- GPU usage: dedicated and shared memory, engine utilization
If your PC is running slow and you’re wondering why, this tab is often where you find answers. For example, if CPU usage is constantly spiking to 100%, you might be running a background task like antivirus scanning or video rendering without knowing.
Mastering the Performance tab is essential to understanding what Windows Task Manager can reveal about system bottlenecks and hardware health—helping you determine whether it’s time to end a task or consider upgrading components.
App History Tab
The App History tab in Windows Task Manager helps users track how much CPU time and network bandwidth each app has consumed over time—especially for Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps installed from the Microsoft Store. This is particularly valuable when you’re trying to pinpoint apps that silently drain system resources or impact battery life on laptops and tablets.
Typical use cases include:
- Detecting background apps that consume high network data
- Analyzing which apps have the most CPU time over days or weeks
- Managing battery-draining UWP apps more effectively
If you’re trying to understand long-term resource usage patterns, this tab answers key questions about system performance history—reinforcing the value of knowing what Windows Task Manager is truly capable of. This tab adds another layer to the answer of What is Windows Task Manager by revealing long-term app impact.
Startup Tab
The Startup tab shows a list of programs configured to launch when Windows boots up. For each entry, it displays the app name, publisher, status (enabled/disabled), and a startup impact score (low, medium, or high).
This section is critical if your PC takes too long to start. Disabling unnecessary startup programs can dramatically improve boot times and reduce early CPU load—especially on older machines.
Using this tab effectively gives you direct control over what runs in the background every time you power on your device, proving again how vital Windows Task Manager is for performance optimization.
Users Tab
The Users tab in Task Manager displays all currently signed-in users and their associated processes and resource usage (CPU, memory, disk, and network). This is especially useful in multi-user environments or shared PCs in offices, classrooms, or households.
For example, if your PC is slow and you discover another user session running a heavy task in the background, you can disconnect or log off that session to reclaim resources. It’s one more reason why knowing what Windows Task Manager is and how to use it matters across both personal and enterprise use cases.
Details Tab
The Details tab offers an advanced, granular view of all running processes on the system. It’s favored by IT professionals for deep process management, thanks to columns showing:
-
- Process ID (PID)
- Status (running/suspended)
- CPU and memory usage
- Thread count
- Base priority
This is also the tab where you can right-click a process to set priority levels or assign processor affinity, letting you control which cores an app can use. If you’re looking to fine-tune app performance—or resolve conflicts from competing processes—this tab is a go-to. If you suspect hardware issues like outdated or malfunctioning drivers, consider pairing Task Manager with Device Manager to further inspect or update specific components.
Services Tab
The Services tab in Windows Task Manager lists all system services currently running or stopped, with descriptions, status indicators, and the ability to start, stop, or restart them.
This is a key area when diagnosing problems related to:
- Windows Update failures
- Network or audio service issues
- Third-party background services not responding
Understanding how to manage services helps you fix deeper system-level problems without needing to reboot or reinstall software—another example of how mastering what Windows Task Manager is enhances both your troubleshooting skills and your system’s stability.
Practical Use Cases and Troubleshooting with Task Manager
- Ending a frozen program: Identify the unresponsive app in the Processes tab, right-click it, and select “End Task” to free system resources.
- Identifying resource hogs: Use the CPU and Memory columns to find apps consuming excessive resources, then evaluate if they should be closed or optimized.
- Spotting malware: Look for unfamiliar or suspicious processes with high resource usage; research process names online or scan with security software.
- Optimizing startup time: Disable non-essential startup programs in the Startup tab to speed up boot performance.
Safety tips: Avoid ending system-critical processes like “Windows Explorer” or services vital for OS stability to prevent crashes or data loss.
Best Practices and Warnings for Using Task Manager
- Do’s: Regularly check task manager if your PC slows down; end tasks only when necessary; disable startup apps to improve boot time.
- Don’ts: Avoid ending critical system processes (e.g., “System,” “svchost.exe”); don’t change process priorities without understanding implications; don’t rely solely on Task Manager to detect malware.
Warning: Improper use may cause data loss or system instability. Always back up work before ending processes, especially if unsure.
Advanced Tips and Customization for Power Users
Power users can customize Task Manager for tailored monitoring and diagnostics. You can add or remove columns in the Details or Processes tabs to display specific metrics like I/O reads, GPU engine usage, or thread count. Context menus offer tools such as “Open file location” to quickly navigate to an executable’s folder or “Search online” to investigate unknown processes. Advanced diagnostics include setting process priority or affinity to control which CPU cores an application uses, helping optimize performance for demanding tasks. Reviewing startup impact scores guides selective enabling/disabling of applications to fine-tune boot speed. Keyboard shortcuts and right-click options further streamline your workflow.

Task Manager Across Windows Versions
Task Manager has evolved significantly from Windows 7 through Windows 11:
- Windows 7: Basic tab layout with limited performance graphs.
- Windows 8: Modern UI introduction with Startup tab and improved app history.
- Windows 10: Enhanced performance metrics, GPU monitoring, and process grouping.
- Windows 11: Streamlined design, touch-friendly interface, and accessibility improvements including high-contrast mode support.
Each version improved usability and feature depth, aligning with contemporary hardware and user needs.
Frequently Asked Questions about Windows Task Manager
Q1: What happens if I end a process in Windows Task Manager?
A: Ending a process in Windows Task Manager will immediately close the associated app or service. This is useful for stopping frozen or unresponsive programs. However, be aware that doing so may result in unsaved work being lost or temporary system instability if you end a critical background task.
Q2: Can Windows Task Manager detect viruses?
A:Windows Task Manager is not an antivirus tool, so it cannot directly detect or remove malware. However, it can help identify suspicious or unknown processes using high CPU or memory—often a sign of malicious activity. For removal, use a dedicated security program like Windows Defender.
Q3: Which tabs in Task Manager show memory usage?
A: The Processes, Performance, and Details tabs all provide insights into memory usage in Windows Task Manager.
- Processes shows memory used per app
- Performance displays overall memory metrics
- Details offers granular data per process including memory consumption
Q4: Is Resource Monitor the same as Windows Task Manager?
A: No. Resource Monitor is a more advanced utility that offers detailed filtering and deeper diagnostics, especially for disk and network activity. Windows Task Manager provides a simpler, more accessible overview—ideal for quick checks and basic troubleshooting.
Q5: What are the most common mistakes users make in Task Manager?
A: Common mistakes include:
- Ending system-critical processes like
explorer.exeorsvchost.exe, which may cause crashes - Disabling unknown startup items without research, which can prevent essential background services from running
Understanding what Windows Task Manager is and how to use it responsibly helps avoid these pitfalls while maximizing its potential.
Other Tools Related to Windows Task Manager
While understanding what Windows Task Manager does is essential, it’s equally important to know when other tools may be more appropriate for advanced diagnostics or automation. Here’s how Task Manager compares to other built-in Windows utilities:
Is there an alternative to Task Manager in Windows?
Yes. In addition to Windows Task Manager, tools like Resource Monitor and Performance Monitor provide more in-depth views of system health. These tools are ideal for advanced users or IT professionals who need more granular, filterable data across CPU, disk, network, and memory activity.
What is Resource Monitor and how does it differ?
Resource Monitor offers detailed, real-time monitoring of processes and resource usage. Unlike Task Manager’s high-level overview, it enables users to filter by individual services, track disk I/O per process, and view associated handles and modules. If Task Manager gives you the summary, Resource Monitor delivers the footnotes.
Should you use Task Manager or command-line tools for diagnostics?
Windows Task Manager is excellent for quick visual diagnostics—ideal for ending unresponsive apps or reviewing system load at a glance. However, PowerShell Cmdlets and Command Prompt tools offer more control for scripted analysis, remote management, or automation tasks in professional environments.
What are other useful Windows troubleshooting utilities?
Alongside Windows Task Manager, the following tools form a powerful diagnostic suite:
- Event Viewer – for reviewing detailed system and security logs
- System Configuration (msconfig) – for boot configuration and startup control
- Performance Monitor – for real-time performance tracking with customizable data sets
When used together, these tools provide a comprehensive view of what’s happening inside your Windows system—and why.
Conclusion
What is Windows Task Manager? It’s more than just a way to end frozen programs—it’s your go-to command center for real-time system insights, diagnostics, and performance control. Whether you’re a tech novice or an experienced user, knowing how to leverage this tool gives you the upper hand in managing system stability, speed, and resource usage.
Here’s a quick recap of what you’ve learned:
- How to open and navigate every tab in Windows Task Manager
- How to diagnose crashes, optimize startup apps, and monitor hardware activity
- When to use Task Manager vs. Resource Monitor or PowerShell
- Common mistakes to avoid and best practices for long-term performance
If you’re serious about maintaining a smooth and secure PC experience, mastering what Windows Task Manager is and how to use it will future-proof your Windows skills.
Want more practical tech tutorials and performance tips?
Visit Softbuzz homepage to explore trending guides and trusted solutions written for users like you.
Or browse related articles in our Windows category to deepen your knowledge on tools like Event Viewer, Safe Mode, and more.
The more you understand your system, the more control you gain—and Windows Task Manager is the perfect place to start.






![VMWare Workstation 15: Ultimate Virtual Machine Experience [Complete Guide 2021] 24 VMWare Workstation 15: Ultimate Virtual Machine Experience [Complete Guide 2021] 23](https://softbuzz.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/cach-tai-vmware-workstation-15-full-key-moi-nhat-2020_softbuzz_14.jpg)
